
The Application of Multichannel Neuro-electrostimulation for
Working Memory and Attention Improvement of Young Subjects
Anna Petrenko
a
and Vladimir Kublanov
b
Ural Federal University, Mira 19, 620002, Yekaterinburg, Russian Federation
Keywords: Attention, Neuro-electrostimulation, Neuroplasticity, N-back, Working Memory.
Abstract: The paper discusses the possibilities of using multichannel neuro-electrostimulation method to improve the
characteristics of attention and working memory of young subjects. It was shown that the results of the test
for assessment of working memory and attention in the experimental group with the use of neuro-
electrostimulation was higher than those in the control and placebo groups. In addition, during the processing
of the functional studies data, such heart rate variability parameters were obtained, the dynamics of which
reflects the positive effect of neuro-electrostimulation. It was found that the effect of neuro-electrostimulation
affects the formation of increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system of the body due to the
intensification of the action of energy processes.
1 INTRODUCTION
In an intensively developing information society, the
need for improving cognitive functions is steadily
growing. In recent years, the active attention of many
researchers has been drawn to the search for new
methods to improve brain function. Improving
cognitive skills is a multifaceted concept involving
the study of the fundamental mechanisms of the brain
functioning at different levels of its organization
(Dresler et al., 2019).
Now there is an active study of factors and
conditions to provide more effective methods for
improving cognitive skills. One of the main
conditions for ensuring the ability to learn is the
active functioning of neuroplasticity processes
(Maslach & Leiter, 2016).
Neuroplasticity is a set of multilevel processes of
continuous morphological and functional
reorganization of the brain, thus ensuring adaptation
to changing external and internal conditions
(Schverer et al., 2018). One of the hypotheses is the
assumption that neuro-electrostimulation allows to
reorganize neural networks by modulating their
connections and is able to modulate higher cortical
functions - to facilitate learning, recognition of visual
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5906-5755
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6584-4544
images, improve memory and decision-making, and
can also be used for neurocognitive rehabilitation
(DARPA, 2016). Thus, one of the promising methods
for improving cognitive skills can be the use of neuro-
electrostimulation methods.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was approved by the local ethics committee
at the Ural State Medical University in accordance
with the protocol number 8 on October 16, 2015.
Practically healthy subjects participated in the
studies.
In previous paper (Kublanov & Petrenko, 2018)
we described in more detail the research
methodology.
2.1 Estimation Method of Attention
and Working Memory
N-back test is selected to estimate of working
memory and attention functions. Step of
memorization is N=2. Subjects work with a sequence
of position and audio stimuli presented one in each
time interval and must give an answer if the current
Petrenko, A. and Kublanov, V.
The Application of Multichannel Neuro-electrostimulation for Working Memory and Attention Improvement of Young Subjects.
DOI: 10.5220/0010395302550260
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 255-260
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
255
stimulus coincides with the element represented by 2
intervals back (dual 2-back test).
The quality of the test was assessed according to
the following parameters: mean response time of
position and audio stimuli, score of position stimuli,
score of audio stimuli, total score.
2.2 Neuro-electrostimulation Method
The ‘SYMPATHOCOR-01’ device is selected as the
multichannel neuro-electrostimulation method.
Device generates spatially distributed field of current
pulses (Danilov et al., 2015; Kublanov et al., 2014)
and it is approved for use in medical institutions of
the Russian Federation and has a state certificate of
the Federal Service on Surveillance in Healthcare and
Social Development № FSR 2007/00757 от
27.09.2007. Applying of the device does not cause
side effects ( Kublanov et al., 2010).
For the current study parameters field of the
current pulses were as follows: the amplitude of the
partial current pulses is 4mA, the pulse duration of the
partial current is 50 microseconds, the frequency of
the partial current pulses is 80 Hz.
The advantage of using this method is the
application of a non-invasive multielectrode
neuroelectrostimulation. The ‘SYMPATHOCOR-01’
device is a mobile and portable device, has the ability
to individually select the parameters of stimulation,
as well as its use is possible simultaneously with other
functional and psychometric tests.
2.3 Sequence of Research Stages
At the first stage of the study, 65 subjects aged 20 to
25 years took part, randomly divided into the
experimental (33 persons), control (10) and placebo
(22) groups. Subjects initially performed the dual 2-
back test in order to determine the baseline values for
attention and working memory parameters.
The sequence diagram of the first stage of the
study is shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Sequence diagram.
№ step Name of step
Duration, min.
1
Background 5
2
dual 2-back test 5
3
Rest 5
4
dual 2-back test 5
5
Background 5
At the second stage of the study subjects of the
experimental group performed simultaneously with
the corrective action of the neuro-electrostimulation
device during 5 day. Subjects of the placebo group
performed dual 2-back test simultaneously with the
placebo stimulation during 5 day. In placebo
stimulation, a sequence of current pulses is formed by
one anode and one cathode, and the target of the
implications is the neck areas in which the presence
of the sympathetic nervous system fibers is minimal.
Subjects of the control group performed a stress
test without corrective action during 5 day.
Table 2: Sequence diagram.
Experimental
group
Placebo
group
Control
group
Duration,
min.
Background 5
neuro-
electrostimula
tion +
dual 2-back
test
placebo
stimulation+
dual 2-back
test
dual 2-
back test
5
Rest 5
neuro-
electrostimula
tion +
dual 2-back
test
placebo
stimulation+
dual 2-back
test
5
Background 5
For experimental and placebo groups ECG signal
was registered at the 1
st
and 5
th
days. The ECG
registration was carried out using
electroencephalograph-recorder «Encephalan -
EEGR-19/26».
«STATISTICA 12.0» software applications were
used for statistical analysis of the obtained data
during study.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Results of the Test Parameters
The variance analysis (ANOVA) of test parameters
was carried out to assess difference between
experimental, control and placebo groups.
During the ANOVA significant changes were
obtained for the mean response time position and total
score variables. The values obtained are reliable at the
level of p≤0,05.
The results of the ANOVA for mean response
time position and total score with the marked ranges
NDNSNT 2021 - Special Session on Non-invasive Diagnosis and Neuro-stimulation in Neurorehabilitation Tasks
256
of standard deviation in the experimental, placebo
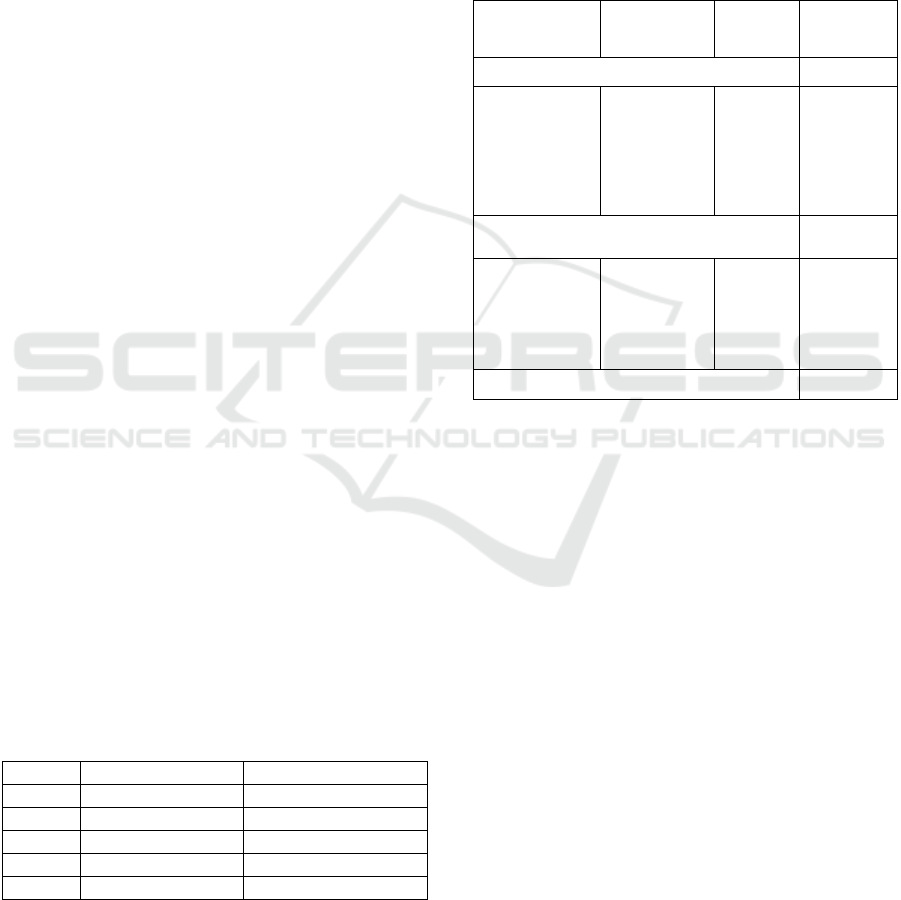
and control groups are presented in Figures 1-2.
Figure 1: Changes of mean response time position for each
groups.
Figure 2: Changes of total score for each groups.
For the experimental group, the test was re-
evaluated after 2 months without the use of neuro-
electrostimulation. The results are presented in
Figures 3-4.
Figure 3: Repeated ANOVA results of mean response time
in the experimental group.
Figure 4: Repeated ANOVA results of Total score in the
experimental group.
According to the primary assessment of the
parameters of the dual 2-back test, the average values
of total score in the three groups was (41 ± 1.9)%.
After the first procedure of neuro -
electrostimulation, the average values of total score in
the experimental group was (58.5 ± 1.9)%, in the
control group - (53.3 ± 3.1)%, in the placebo group -
(52.7 ± 2.1)%. At the same time, there is the greatest
increase in total score values - in all three groups.
A significant difference between the three groups
is observed as early as 3
rd
day of the neuro-
electrostimulation procedure. The average values of
total score in the experimental group after the 3
rd
neuro-electrostimulation was (69.6 ± 1.8)%, in the
control group - (63 ± 5.6)%, in the placebo group -
(63 ± 2.3)% .
Also, after data processing the, significant
changes were obtained in the mean response time of
position stimuli.
According to the initial assessment, the mean
response time of position stimuli in the three groups
was (1.39 ± 0.06) sec.
On the 3
rd
day, the mean response time of position
stimuli in the experimental group was (1.19 ± 0.03)
sec., in the placebo and control groups - (1.24 ± 0.05)
sec. and (1.26 ± 0.06) sec. respectively.
By re-evaluating the test parameters in the
experimental group after 2 months, the results are
preserved both in the mean response time total score.
3.2 Results of HRV Analysis
Heart rate variability (HRV) data were obtained from
the recorded ECG signal. For data analysis, the 64
parameters of HRV were obtained using in-house
software in Python (V. Kublanov & Dolganov, 2019).
Further, artifacts and outliers were excluded and
The Application of Multichannel Neuro-electrostimulation for Working Memory and Attention Improvement of Young Subjects
257
calculated the mean values and the corresponding
standard deviations for each group.
The ANOVA for the HRV parameters was carried
out during the 1
st
and 5
th
procedures of neuro-
electrostimulation and placebo stimulation in the
experimental and placebo groups to assess functional
changes.
Significant changes were obtained at the level of
p≤0.05 in the following variables: Stress index or
index of regulatory systems tension (SI), index of
autonomic balance (IAB), autonomic rhythm index
(ARI), indicator of the adequacy of regulation
processes (IARP). The obtained data are presented in
Table 3.
Table 3: Values of HRV parameters for the experimental
and control groups on 1
st
and 5
th
days.
Experimental
group
Placebo
group
day 1 5 1 5
SI
mean 150,63 156,96 129,92 114,06
std 7,4 7,45 13,7 13,28
IAB
mean 215,43 224,22 192,41 173,32
std 9,37 9,43 17,34 16,8
ARI
mean 7,35 7,53 6,62 6,29
std 0,23 0,23 0,42 0,41
IARP
mean 51,58 52,76 48,58 44,69
std 1,39 1,4 2,57 2,49
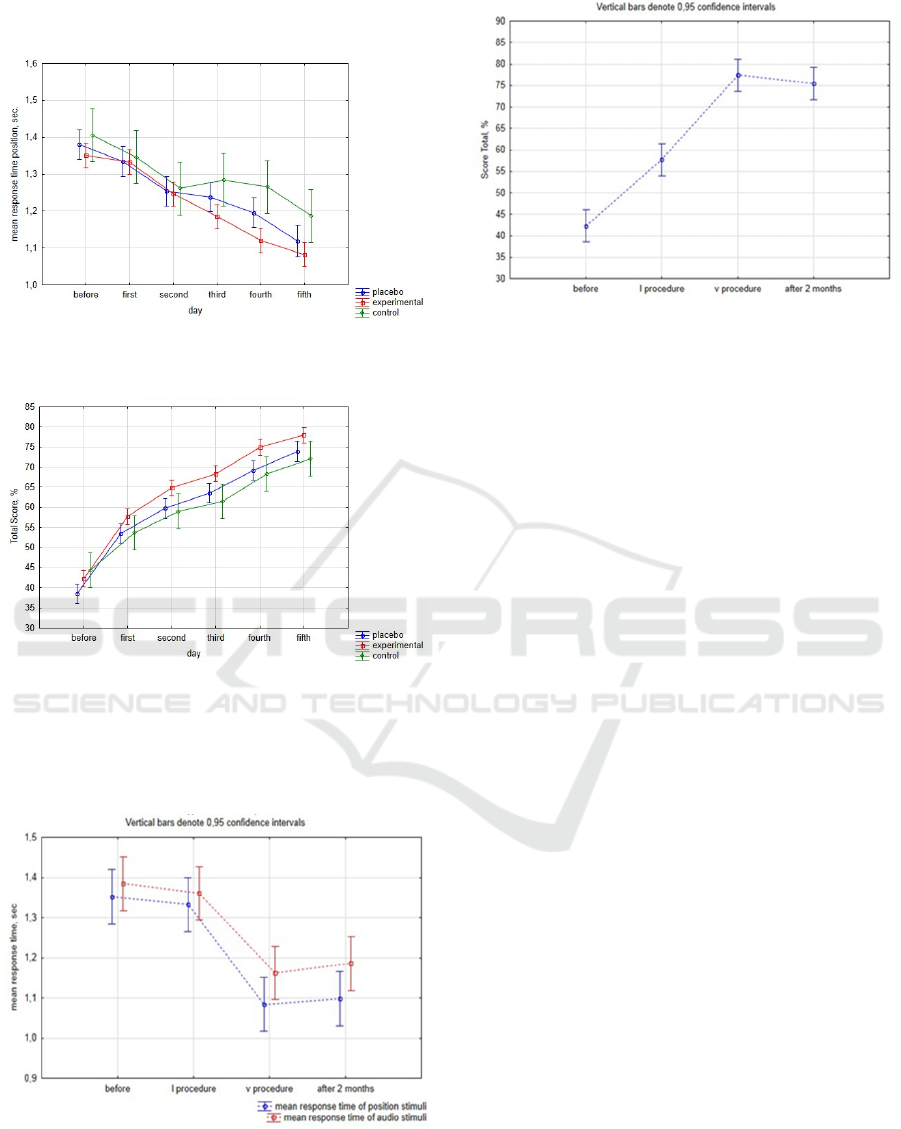
The results of analysis of variance are shown in
Figures 5-7.
Figure 5: ANOVA results of ARI at the first and fifth days
in the experimental and placebo groups.
Figure 6: ANOVA results of IARP at the first and fifth days
in the experimental and placebo groups.
Figure 7: ANOVA results of IAB at the first and fifth days
in the experimental and placebo groups.
Figure 8: ANOVA results of SI at the first and fifth days in
the experimental and placebo groups.
Stress index (SI), index of autonomic balance
(IAB), autonomic rhythm index (ARI), indicator of
the adequacy of regulation processes (IARP) reflect
the degree of adaptation of the cardiovascular system
to various factors (Baevsky & Ivanov, 2001).
Autonomic rhythm index (ARI) reflects the
balance of regulation of the cardiovascular system by
the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the
autonomic nervous system. During the 5
th
procedure
of neuro-electrostimulation parameter ARI in the
NDNSNT 2021 - Special Session on Non-invasive Diagnosis and Neuro-stimulation in Neurorehabilitation Tasks
258

experimental group was higher on 20% than in the
placebo group. An increase of the ARI value indicates
an increased activity of the sympathetic nervous
system in the subjects of the experimental group.
The index of autonomic balance (IAB) shows the
ratio of the effect on the cardiovascular system of the
sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. For
subjects of the experimental group, there is an
increase in this indicator at the 5
th
procedure of neuro-
electrostimulation compared with the placebo group.
This indicates an increase in the role of the
sympathetic nervous system. For subjects in the
placebo group, the IAB score is lower; therefore, the
parasympathetic nervous system has a predominant
effect.
The indicator of the adequacy of regulation
processes (IARP) allows one to determine the effect
on the sinus node of the sympathetic section and is the
most stable indicator. For subjects, this indicator
during the 5
th
procedure of neuro-electrostimulation
was 52.76 ± 1.4, which is higher than those in the
placebo group - 44.69 ± 2.49. The obtained data
indicate an increase in the sympathetic part of the
nervous system through the action of neuro-
electrostimulation; the influence of the sinus node on
heart rate becomes more pronounced.
The stress index (SI) indicates the degree of
influence of the nervous system on the work of the
heart. For the subjects of the experimental group,
there is an increase of this indicator relative to the
placebo group, which indicates the formation in the
body of an increased activity of the sympathetic
division and an increase in the degree of
centralization of heart rate control. This may indicate
the effect of the influence of neuro-electrostimulation
on the regulation of sympathetic nervous structures,
which reflects the activation of ergotropic
mechanisms of regulation and an increase in the
intensity of energy processes.
4 DISCUSSION
The results of the study showed that the use of neuro-
electrostimulation of the peripheral nervous system in
conjunction with a dual 2-back test improves working
memory, reaction time and attention parameters. It
was shown that performance of three neuro-
electrostimulation procedures is enough to see
significant intergroup differences in the parameters of
the performed N-back test.
The advantage of the proposed technique for
increasing the level of concentration and attention is
the use of a non-invasive multielectrode neuro-
electrostimulation system implemented in the
‘SYMPATHOCOR-01’ device. A possible
mechanism of action is the activation of peripheral
nerves, which in turn facilitate and strengthen neural
connections in the brain. The activation of peripheral
nerves occurs using neuro-electrical stimulation of
the cervical ganglia of the sympathetic nervous
system and the corresponding pathways of the nerve
formations.
Furthermore, while processing the data of
functional studies, HRV parameters were obtained,
the dynamics of which reflects the positive effect of
neuro-electrostimulation. It was found that the effect
of neuro-electrostimulation affects the formation of
increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system
of the body due to the intensification of the action of
energy processes.
To increase the reliability of intergroup
differences in other functional parameters of HRV, it
is necessary to increase the number of samples in each
group.
5 CONCLUSION
During the study, a technique was developed for
increasing the level of attention and working memory
using neuro-electrostimulation. The advantage of this
method is the use of a mobile and portable unit of
non-invasive neuro-electrostimulation with the
possibility of individual selection of neuro-
electrostimulation parameters. The technique allows
you to combine neuro-electrostimulation with other
loads (for example, with psychometric tests), as well
as monitor the functional state of a person using ECG
registration.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The reported study was funded by RFBR according
to the research project № 18-29-02052.
REFERENCES
Baevsky, R. M., & Ivanov, G. G. (2001). Analysis of heart
rate variability using various electrocardiographic
systems: A guidelines. 24, 65–68.
Danilov, Y. P., Kublanov, V. S., Retjunskij, K. J., Petrenko,
T. S., & Babich, M. V. (2015). Non-invasive multi-
channel neuro-stimulators in treatment of the nervous
system disorders. BIODEVICES 2015 - 8th
International Conference on Biomedical Electronics
The Application of Multichannel Neuro-electrostimulation for Working Memory and Attention Improvement of Young Subjects
259

and Devices, Proceedings; Part of 8th International
Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems
and Technologies, BIOSTEC 2015, 88–94.
https://doi.org/10.5220/0005200000880094.
DARPA. (2016). Targeted Neuroplasticity Training (TNT).
Biological Technologies Office, 36p.
Dresler, M., Sandberg, A., Bublitz, C., Ohla, K., Trenado,
C., Mroczko-Wąsowicz, A., Kühn, S., & Repantis, D.
(2019). Hacking the Brain: Dimensions of Cognitive
Enhancement. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 10(3),
1137–1148.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00571
Jaeggi, S. M., Studer-Luethi, B., Buschkuehl, M., Su, Y.-
F., Jonides, J., & Perrig, W. J. (2010). The relationship
between n-back performance and matrix reasoning—
Implications for training and transfer. Intelligence,
38(6), 625–635.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2010.09.001.
Kublanov, V., & Dolganov, A. (2019). Development of a
decision support system for neuro-electrostimulation:
Diagnosing disorders of the cardiovascular system and
evaluation of the treatment efficiency. Applied Soft
Computing, 77, 329–343.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.01.032.
Kublanov, V. S., Chernykh, O. A., Purtov, K. S., & Babich,
M. V. (2014). The hardware-software system for study
of microwave radiation biological effects. 2014 24th
International Crimean Conference Microwave
Telecommunication Technology, 1038–1039.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CRMICO.2014.6959749.
Kublanov, V. S., Petrenko A. A. (2018). On the possibilities
of neuro-electrostimulation for increasing learning
parameters. 2018 11th International Joint Conference
on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies,
338-344. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006592503380344.
Kublanov, V. S., Shmirev, V. I., & Shershever, A. S.
(2010). About innovative possibilities of the device
SYMPATOCOR in management of functional disorders
of autonomic and central nervous system in neurology.
4, 60–64.
Maslach, C., & Leiter, M. P. (2016). Burnout. In Stress:
Concepts, Cognition, Emotion, and Behavior (pp. 351–
357). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-
800951-2.00044-3.
Pelegrina, S., Lechuga, M. T., García-Madruga, J. A.,
Elosúa, M. R., Macizo, P., Carreiras, M., Fuentes, L. J.,
& Bajo, M. T. (2015). Normative data on the n-back
task for children and young adolescents. Frontiers in
Psychology, 6, 1544.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01544.
Schverer, M., Lanfumey, L., Baulieu, E.-E., Froger, N., &
Villey, I. (2018). Neurosteroids: Non-genomic
pathways in neuroplasticity and involvement in
neurological diseases. Pharmacology & Therapeutics,
191, 190–206.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.06.011.
NDNSNT 2021 - Special Session on Non-invasive Diagnosis and Neuro-stimulation in Neurorehabilitation Tasks
260
