
Enhancing the Teaching of Informatics through
Engaging Experience
Martin Cápay
Department of Informatics, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Constantine the Philosopher University, Nitra, Slovak Republic
Keywords: Cognitive Engagement, Experience Activities, Discovery Learning, Physical Computing.
Abstract: There are plenty of learning approaches today, which are based on well-known educational theories, and
which try to encourage students to active participation in the educational process. Educational activities
designed to acquire knowledge from experience lead students to make own abstract or mental models. This
paper describes a set of experiments being conducted in the delivery of computer science courses using the
experience to supplement or replace the traditional model of the lectures. Using physical computing
concepts allows students to develop concrete, tangible products. According to our experience, we should
conclude that children really learn from their attempts and errors even in computer science classes. Our
vision is closest to the experimental learning model do – reflect – apply supported by using well-designed
questioning. Abstraction and conceptualization are preceded by the visualization and manipulation of the
objects or commands. The great benefit of “getting physical“ is a holistic view of computer science which
encourages creativity, promotes learning by doing and even engaging the whole mind and body. We
conclude that relatively simple teaching aid, mobile devices, special hardware, and well-designed online
programming activities could help to explain even abstract computer science underlying concepts through
the experience sometimes more effectively than through instructional model.
1 INTRODUCTION
The student’s disengagement is a huge problem and
challenge for teachers everywhere. When we think
of student engagement in learning activities, it is
often convenient to understand engagement with
activity as being represented by good behaviour,
positive feelings, and, above all, student thinking
(Fredricks, 2014). The engagement takes an
important role also for achievement, performance,
motivation and also for intellectual development.
When students are fixed only for the preference of
getting a good grade, they often select less
challenging or somewhat familiar tasks. Contrary,
students with different goal preferences select tasks
that will enable them to improve their abilities and
skills even if it means being faced with mistakes
(Chen and Pajares, 2010). We need to develop the
internal motivation of the young people and sustain
their interest in acquiring required skills (Skalka and
Drlík, 2018). Modern technology, such as drones
can be used as a motivational tool for engaging
students (Voštinár et al. 2018). We assume the goal
preferences of students are influenced by the level of
engagement and participation during the school
years. Students need to be encouraged to carry out
the responsibility and doing all without worries to
make mistakes. In science, and also especially in
computer science, it is critical to the success of the
educational process that students become actively
engaged in it, rather than passive recipients of the
presented knowledge.
In spite of that, the critics believe that constructivist
methods may result in potential misconception, a
modern learning theory takes place in problem-
solving situations when the learners developed new
knowledge on their past experience and existing
knowledge to discover facts and relationships and
new truths to be learned. In contrast to the
transmissions models, students may likely remember
more concepts and knowledge discovered on their
own.
Therefore, the main aim of the paper is to
describe several experience-based activities
designed for the teaching computer science topics at
the primary and secondary schools, which are based
on the several main characteristics of the most
known learning theories and approaches. This paper
Cápay, M.
Enhancing the Teaching of Informatics through Engaging Experience.
DOI: 10.5220/0007759104530460
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2019), pages 453-460
ISBN: 978-989-758-367-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
453

describes a set of experiments being conducted in
the delivery of the content using experience-based
learning approach to supplement or replace the
traditional model of the lectures. Students interact
with the world by exploring and manipulating
objects, wrestling with questions and controversies,
or performing experiments.
2 LEARNING BY EXPERIENCE
There are plenty of learning approaches today,
which are based on well-known educational theories,
and which try to encourage students to active
participation in the educational process. The
following approaches can be considered as examples
of learning approaches, which are common in
computer science: Problem Based Learning (BL),
Project BL, Discovery Learning, Guided Discovery
Learning, Design BL, Student-Centered Learning,
Inquiry BL, and Experience BL. The distinctions
between these approaches are in some respects quite
fine. Computer science is well-suited for the
majority of mentioned learning approaches. The
discipline itself is changing so rapidly, that it is
difficult to introduce students to it without involving
them into the creative process (Foley, 1999).
The 5E model (Engage, Explore, Explain,
Elaborate, and Evaluate) encourages students to
explore science concepts and phenomena, construct
their understanding through self-reflection and
interaction with peers, and relate those
understandings to other science concepts so that they
can reconsider and appropriately change the way
they understand reality (Bybee, 2015). In the Next
Generation Science Standards (NGSS), the teacher
plans learning experiences in which students
construct knowledge through exploration and
investigation. The framework envisions that students
will gradually deepen their understanding of
scientific ideas over time by engaging in practices
that scientists and engineers use (NGSS). Despite
the positive result of using the 5E learning model
science in facilitation and retention in natural
science courses (Ajaja and Urhievwejire 2015),
constructivist learning environment may not cause
the same effects for each (Feyzioğlu and Ergin,
2012).
In Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory the
experience from natural that observation something
is happening, and reflection on that are then
incorporated into the theoretical knowledge that the
person already possesses. Kolb defines experiential
learning as "the process whereby knowledge is
created through the transformation of experience”
(Kolb, 1984). Effective learning is seen as when a
person progresses through a cycle of four stages:
having an individual experience followed by the
observation and reflection on that experience, which
leads to the formation of abstract concepts (analysis)
and generalizations (conclusions) which are then
used to test hypothesis in future situations, resulting
in a new experience. Experience learning theory is
intended to be a holistic adaptive process on learning
that merges experience, perception, cognition, and
behaviour. It is based on a set of assumptions (Boud
et al., 1996) that experience is the foundation of, and
the stimulus for, learning; learners actively construct
their own experience; learning is a holistic process;
learning is socially and culturally constructed;
learning is influenced by the socio-emotional
context in which it occurs. Experimental learning
theory provides a solid foundation for leadership
education (Guthrie and Jones, 2012).
The experience-based learning (EBL) is based on
assumption, that the experience of the learner
occupies a central place in all considerations of
teaching and learning. This experience may
comprise earlier events in the life of the learner,
current life events, or those arising from the learner's
participation in activities implemented by teachers
and facilitators.
A key element of experience-based learning is
that learner analyses her experience by reflecting,
evaluating and reconstructing it (sometimes
individually, sometimes collectively, sometimes
both) in order to draw meaning from it in the light of
the prior experience (Foley, 1999)
Students need to be encouraged to engage and to
participate. This is important because authentic
engagement may lead to higher academic
achievement throughout student life (Zyngier, 2008).
According to Schlechty (2001), students are engaged
when they are involved in their work, persist despite
challenges and obstacles, and take visible delight in
accomplishing their work.
The deepest levels of learning, according to
Bloom's Taxonomy, happen when students are
constructing, creating, and getting hands-on with
learning materials. The great benefit of "getting
physical“ is a holistic view of computer science
(across hardware and software) which encourages
the creation of projects (crafting), promotes learning
by doing and engaging the whole learning mind and
body (Jin et al. 2016). The combination of physical
construction with computer science and coding has a
variety of aspects and outcomes including creativity
(Sentence et al. 2017), cognitive load (DesPortes et
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
454
al. 2016), student perceptions (Dafai et al., 2014)
and motivation (Kaloti-Hallak, 2015). Physical
computing as we call a process of creatively
designing tangible interactive objects or systems
using programmable hardware (Sentence et al.
2017), even helps students to gain confidence in
programming (Rubio et al.). It can be much more
positive than a more traditional screen-based
experience because of the focus on ideas, rather than
restrictions (Sentence et al. 2017), students
appreciate building real, tangible devices and report
that physical computing platforms stimulate their
creativity (Hodges et al.)
2.1 Methodology of Learning through
the Experience
The significant aspect of the learning model based
on experimentation is that explanation follows
experience. Students are involved in more than
listening and reading. They are developing skills,
analysing and evaluating evidence, experiencing and
discussing, and talking to their peers about their own
understanding. Teachers need to adjust not only the
educational materials but also the way of leading the
course. Our suggestion is followed.
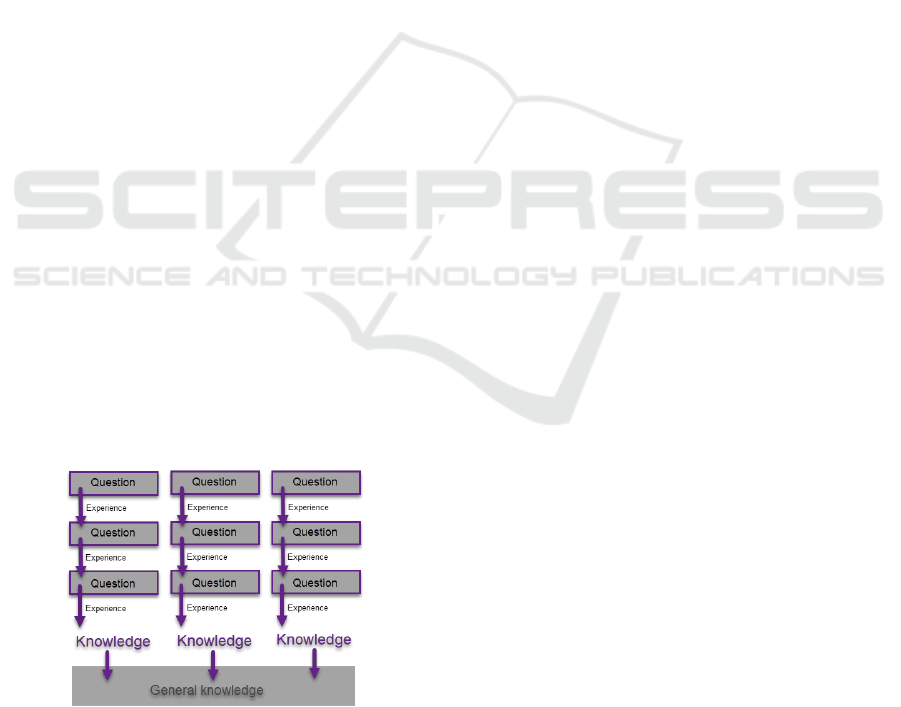
Firstly, the main goal of the activity must be
stated. The content of the current lesson needs to be
divided into well-designed parts with specific goals,
according to the current level of knowledge to all
students. The goals of each part must be clear and
reachable. Reaching of each specific goal must lead
to generalization. The sequence of activities based
on experience, that involves "doing something",
should be used to gain general knowledge (Figure
1). The targeted questioning of students is the most
important and mandatory either at the beginning
(open question) or at the end (generalize question) of
the experience.
Figure 1: Experience as a part of developing knowledge.
Students experience is a precondition for
answering the predesigned questions important to
fluent transition to the next lesson topic.
The knowledge gained by specific activity must
be developed during the followed, more abstract
activity. For example, if we want to explain how 3D
technology works, we will do some short activities
to explain several facts about the eyes, brain, filters,
and stereoscopic illusion. Students discover the
principles of 3D by their own reasoning. Our vision
is closest to the experimental learning model “Do –
Reflect – Apply” supported by using well-designed
questioning. Abstraction and conceptualization are
preceded by the visualization and manipulation of
the objects or commands.
The main goal of the paper is to present how to
manage the lessons to achieve student’s engagement
by experimenting with hands-on material or tangible
devices. This process was evaluated several times,
we observe how to ask the question and which
activity need to be followed. We present the
description of this question-experience-knowledge
process on different types of activities.
3 EXPERIENCE BASED
LEARNING IN COMPUTER
SCIENCE
When we design learning activities, we should take
more aspects into account. The learning activities
varied in their contents, educational goals of the
learning activities, various teaching/learning
methods and using a various aid such as physical
objects or digital devices (Lovászová et al. 2015).
The main purpose of this section is to describe a
set of well-designed learning activities that tried to
motivate and engage the students in improving their
level of knowledge. The activities were evaluated
during the regular lessons, non-formal workshops or
summer camps. They were designed to foster
computational and logical thinking.
3.1 Hands-on Activities
Elementary school children are too young for the
traditional approach to teaching concepts. We need
to encourage them to visualize the problem and use
their imagination in deriving the solution (Edwards,
2004). Students could develop their ability to
understand and apply the fundamental principles on
which computers and networks operate through
Computer Science Unplugged Activities. It is a
collection of free experiential learning activities that
teach Computer Science through engaging games
and puzzles that use cards, string, crayons and lots of
Enhancing the Teaching of Informatics through Engaging Experience
455

running around. The activities tend to be
kinaesthetic, often involving teamwork (Bell, 2010).
We prepared a group of activities how the data is
traveling through the monitor, computer, and
converter to the Internet. The main goal of our
approach was to present binary notation, to
understand the representation of characters using
ASCII standards, how important is to represent each
binary number using the same numbers of bits, the
transformation the digital into the analog signal, how
to protect the data during transmitting (encryption
and decryption) and to sort them using sequential
and parallel algorithms. All activities were prepared
as computer science unplugged supported by
designed questions. An X-binary coding of alphabets
should be used as an example of engaged activity.
We let the student draw up the rules. Question: “If I
want to send the email, how will I encrypt the
alphabets?” They usually set a rule that alphabets
will be represented by numbers and students already
know how to write the numbers in binary notation
(former activity). Question: “How to code A, B, C ...
and Z?” Students probably suggest coding A as 1
and Z as 26. Question: “What if I suggest own
coding, for example, A as 10.” After the discussion,
students must state a common rule for all alphabets
for both parts of communication. They found out the
concepts of standardization. Each part of the
communication needs to have the same rules for
coding. Question: “Here is your coding table. Are
you able to encrypt the text message to binary code
notation and vice versa?” Each group encrypts own
message using binary notation. After that groups
swap the messages and try to decrypt the message
using the same coding table. In most cases, they are
not able to write the original message. Question: “If
you use the same coding table and the same
notation, why are you not able to decode the original
message?" They argue and discuss the process of
encryption. The most usual mistake is that each
group decided to use a different count of bits or kept
out the zeros at the beginning of the message (Figure
2).
Figure 2: Attempts to decoding the binary message.
Instead of that, each group has the same coding
table they had not the same instruction for binary
notation. They realized that coding table without
common rules of x-bit representation is not enough.
Only after this activity, the one possibility of coding
is presented. ASCII is the 7-bit code American
Standard Code for Information Interchange.
This activity was realized several times at
primary school (11 year-olds: 15 participants; 14-15
year-olds: 40 participants), high school (16-17 year-
olds: 30 participants). Finally, we prepared the
workshop for the in-service teachers (20
participants). The activity should take at least one
lesson. We had a collection of such kind of
activities, so we usually try to connect more lessons
to have a block of activities. The effectiveness of the
approach was evaluated with teachers who teach the
pupils. Most of the theme continuously used this
approach during the lessons. They answered that
students are very satisfied and happy to do this
activity.
We can deduce certain experiential activities
conclusions. We have noticed that most pupils are
active and voluntarily involved in teaching. During
the realization, we are asked a few questions that
were in most cases answered correctly, sometimes
surprisingly fast. Presented activity was preceded by
another one, the transformation of numbers from
binary to decimal (and vice versa). After the
finishing of the activities, even the youngest
participants could write the simple numbers in
binary form without using the calculators.
3.2 Robotics with Mobile Devices
Developing of the robotic model involves the
design, programming and construction phases,
which develop different knowledge, skills and
abilities in the area of problem solving, teamwork,
but also the development of logical thinking, social
skills and the ability to plan and test the procedures
and debug solutions. There are many robot kits
based on different principles of programming and
target groups available today. Preschool children
handle programmable toys (Bee-bot, Blue-Bot).
They directly operate with the toy by entering the
sequence of limited instruction. School children
could handle various types of programmable robots
(Ozobot Bit, Ozobot Evo, Edison). Despite the
possibility to create own program, there is no
possibility for extending its functionality through
sensors. Despite the fact, these toys open a big
opportunity for EBL, we want to describe the
activity based on robots that widened programming
instruction and the possibility to extend their
abilities by connecting external sensors. LEGO
MindStorms based on graphical language is an
example of such kind of set. The NXT robotic kit
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
456

model has been widely spread out in Slovak schools.
The kit contains the small computer that was
programmable only via cable connection with a
computer. Even a basic project uploading to the
main brick took more time that was needed to be
engaged. Plugging and unplugging the robots was
boring and discouraging at the beginning of the
learning, keep in mind that not all children were
purely interested in programming. The situation was
dramatically changed when the EV3 version,
programmable using the mobile technology, was
released. All teaching aids should be mobile,
connected wireless via Bluetooth. So the lesson
should be more interactive organized even outside
the computer lab.
The researched questions for students are
followed. Use the mobile application to observe the
input and output data from ports. Question: “Could
you estimate the units in which the sensors collect
the data?” Students may manipulate with motors and
sensors, change the surrounding of the robots and
reactions are immediately shown on the tablets.
Question: “How the motors behave when the robot
goes forward (backward), forward left/right or just
rotate on the spot?” They learn practically how
motors behave via interactive remote control.
Question: “How to move the robot without the
remote control?” A programming environment is
iconographic based on drag and drop strategy.
Touchscreen technology allows students to interact
with tablet computers in a more natural and
immediate manner. They experience several
commands for a robot moving. Question: “Which
commands and in which order do you need to
simulate a car is going out of petrol?” They must
change the power of motors, experience how to
change the displayed picture and played sound.
Application highlights the currently executed
command, so students can easily follow the program
flow and experiment with the command which
freezes the execution flow. Question: “How to move
the robot forward until it comes to white colour?
How does the robot know that the sensor is crossing
the white colour?” The students need to come with
the theory we do not know the length of the moving
in advance. The motor must switch on before and
switch off after the moving. They learn how to
implement the waiting for data from different
sensors.
The students manipulate directly with the robots
connected to the tablet via Bluetooth without the
knowledge of any theoretical bases (Figure 3). It is
intuitive and easy to use. The response is quick, so
students could experiment more times during the
lesson. The more tries they have, the more
knowledge could be inquired by own
experimentation, without receiving the specific
instructions on how to finish their tasks.
We conclude that after finishing the work, the
students were able to connect the robot and control it
using a digital controller, create a simple sequence
of commands in the iconographic language and to
properly use the data coming from the sensors. The
direct interaction with the robot is the biggest
advantage of robotics with a mobile device.
Robotics with tablets is much better than the
combination of robots and computer. The lesson is
much more dynamic, and students like it. Touching
the screen means much more direct interaction with
a device than using a traditional input device like a
keyboard and a mouse.
Figure 3: Programming of EV3 robot connected to the
tablet via Bluetooth.
In comparison with the desktop version, the
mobile development environment has only a subset
of commands. The more complex problem should be
probably complicated to solve via the mobile
environment. However, a tablet is better for the first
introductory classes. It is easier for students to
understand the concepts.
This activity was realised several times at
university (20-22-year-olds: 30 participants), at
computer science summer school (11-14-year-olds:
80 participants) and finally, we prepared the
workshop for the in-service teachers (10
participants). Based on our experience we can
conclude the university students were less flexible as
students from the primary school. Primary school
students were more engaged and motivated; they
even try to formulate new tasks.
3.3 Robotics on Mobile Devices
Ozobot is the miniature programmable robot with
the own intelligence based on randomly generated
decisions. Ozobot will follow Black, Blue, Red and
Green colours. It is able to recognize the colouring
commands by using sensors. At the lowest level of
programming, we can draw a path along which
Enhancing the Teaching of Informatics through Engaging Experience
457
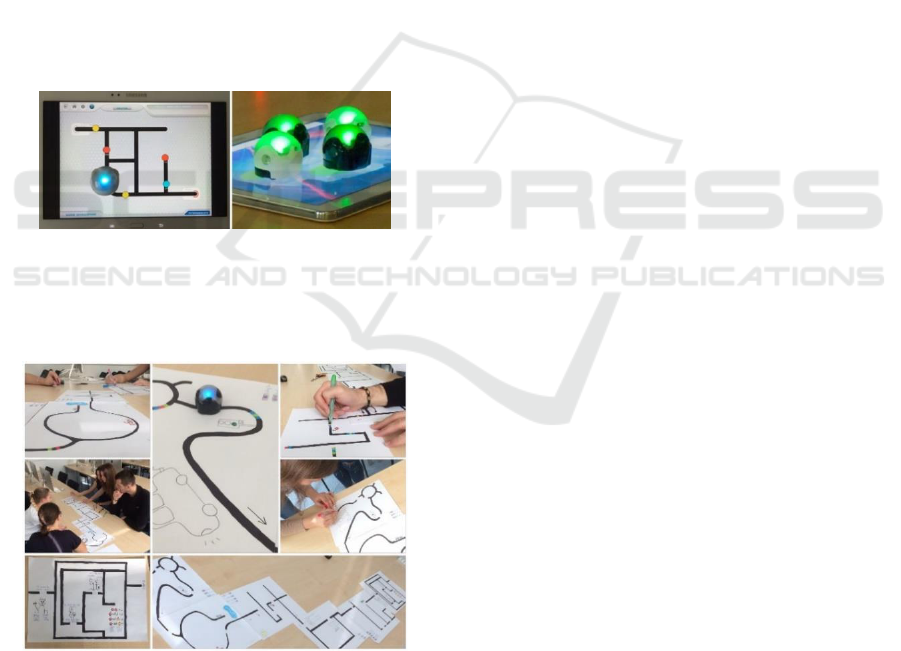

Ozobot passes. Question: “Based on which principle
is the Ozobot moving?” The students have to found
out, the robot randomly decides where it wants to
go. The official application OzoPath and OzoLuck
are interactive games to present a random behaviour.
Question: “How the commands influence the robot
moving?” The game OzoDraw allows us drawing a
path with a finger directly on the tablet screen. The
robot recognizes specific combinations of coloured
commands (ozocodes) on the basis of which we can
control the direction, speed, timing and special
moves. Students can add flashing codes to the path
(e.g. Fast, Turn Left, Tornado, UTurn etc.). Ozobot
performs prescribed operations immediately after the
reading the code, and so the activity is dynamic and
interactive. Question: „Are you able to navigate the
robot to the final destination in the labyrinth using
all of the limited set of commands?” Students use
the proposed labyrinths and a predefined set of
available ozocodes. The aim is to construct a
deterministic algorithm of moving by placing the
ozocodes before the crossroads (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Programming Ozobot using the tablet.
After the experiencing students should prepare
their own paper labyrinths with the extra story
behind (Figure 5.).
Figure 5: Labyrinth with story and sub-tasks.
The math, logic or even a joke could be
included. Students solve the other labyrinth, using
coloured markers by adding the ozocodes. They
need to decide where to increase a speed level, to
decrease a speed, where to turn or where to make a
winner dance. We can achieve the highest level of
programming through an online visual programming
environment OzoBlockly. From the teacher’s
perspective, the Ozobot is an excellent tool for
introductory lessons of robotics.
This activity was realised several times at
primary school (11-year-olds: 30 participants), at
computer science summer school (11-14-year-olds:
40 participants) and finally, we prepared the
workshop for in-service teachers (20 participants).
We can deduce certain experiential activities
conclusions. Ozobot is a simple robot without the
need to design a model, offering a wide range of
programming options. It has a miniature size and a
real resistance to falls. The robot is suitable for the
second grade at the elementary school, but it can
also cover the needs of the secondary school
curriculum in an appropriate range and form. It
supports a wide range of activities.
3.4 Physical Computing with BBC
Micro:bit
BBC Micro:bit (Fig. 6) is a tiny, pocket-sized code
able physical computing device, programmable
computer, a small battery powered circuit board,
designed to make learning and teaching a younger
audience (Cápay and Klimová, 2019). It can be
programmed via a desktop PC, laptop or tablet
through block-based language, MicroPython or
JavaScript. In comparison with most sophisticated
hardware (such as Arduino and Raspberry),
micro:bit is powerful even without any extensions. It
consists of the ARM chip, memory, buttons,
accelerometer, magnetometer, light sensor,
Bluetooth and pins. Using the crocodile clips, we
can extend the possibilities of this device (Hodges et
al., 2013).
The most interesting micro:bit aids we have
experienced was the Adafruit NeoPixel Digital
RGBW LED Strip. Each LED is colored and
programmable, where every color is made as a mix
of red, green and blue color. We use this strip to
teach python lists by creating the Christmas lights.
Question: ”How to colour the strip using the RGB
color model?” According to the pre-prepared code,
where the first LED is already switched on, students
need set to all unlighted LED colour firstly. They
can experience a wide color spectrum. Question:
”How to make a falling snow effect?” They need to
use a loop concept and found out how to switch off
the LEDs. If we want to switch off LEDs we need to
set the black colour and switch on the LEDs.
Question: ”How to make a rainbow that is rotated in
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
458

the loop?” The list must be shifted to the right or to
the left. Question: ”How to make a sparkling
effect?" The concept of a randomly chosen colour
for each LED in the infinity loop must be
discovered.
Figure 6: The microcontroller micro:bit with clips and
LED strip.
We can upgrade the project by creating the
remote control micro:bit, that can be used also like
the effect chooser.
We asked 53 high school students (16-19-year-
olds) several questions in the questionnaire (Cápay
and Klimová, 2019). It was found that the micro:bit
encourages students to work creatively; it is a great
motivator in the classroom. After the first use of the
programming with hardware concept, we noticed the
rise of the motivation to learn programming even
among the ‘non-informatics' pupils, among the girls
and the in-service teacher. We conclude that using
BBC micro:bit is the right decision for those who
want the powerful device to learn programming and
to understand the principles of how the hardware
works at the same time. Programming of micro:bit
microcontroller makes computer science fun and
tangible. Students are engaged because the program
interacts with the outside world through shaking,
tilting, and plotting the LEDs.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Experience-based learning is usually connected with
the natural sciences such as physics, biology or
chemistry. We described several examples, how to
introduce the concepts via experience in computer
science teaching.
Visualization of abstract concepts through
computer science unplugged, as non-formal
education, is an issue that could change the view of
computational thinking. Also, the card tricks should
explain the standard programming concepts such as
shifting, searching and sorting or controlling
checksum. It has been shown that these activities are
helpful. The positive influence of a teacher is a
positive outcome.
Portability, touchscreen interfaces and various
sensors of the tablets provide a big opportunity for
collaborative learning out of the classroom
environment. There are a lot of mobile applications
in stores designed for developing algorithmic
thinking and even programming thinking from early
childhood. The tablets within the computer science
curriculum contribute to the intrinsic motivation of
students. The tablets should be used not only as a
learning tool but also in location-based games, real-
time questioning, and programming.
Evaluation of physical computing concept in
formal education was experienced. We observed that
supporting the programming lesson by using a tiny
programmable computer with a set of sensors and
LEDs is the right way to engage students. We can
prepare a set of tasks presenting the programming
concept using physical computing in such a way that
pupils need to change the sitting activity by playing
activity or hands-on activity realized besides.
Tangible projects are not only engaging and
enjoyable to work on, but also effective in
demonstrating abstract programming concepts for
the beginners.
Programming of micro:bit microcontroller makes
computer science fun and tangible. Students are
engaged because the program interacts with the
outside world through shaking, tilting, and plotting
the LEDs.
According to our experience, we should
conclude that children really learn from their
attempts and errors even in computer science
classes. Generalization should be made after the
experience based on learning tasks. Students used
many tools intuitively. They provide a big
opportunity to discuss openly. It is also important to
choose the topic correctly; not all computer science
content is possible to present only by experience. On
the other hand, teachers should ensure that activities
are designed and carried out in such ways that offer
each learner the chance to engage in the manner that
suits her to the best.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The research leading to these results has received
funding from the project Innovative Methods in
Programming Education in the University Education
of Teachers and IT Professionals (KEGA 029UKF-
4/2018).
Enhancing the Teaching of Informatics through Engaging Experience
459

REFERENCES
Ajaja P. O., Urhievwejire O. E. Effects of 5E learning cycle
on students achievement in biology and chemistry.
Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 01 January
2012, Vol.7(3).
Bell T., Witten I., Fellows M. 2015 Computer Science
without a computer. Aviable at: http://csunplugged.org/
Boud D., Cohen R., Walker D. 1996 (eds) Using Experience
for Learning Buckingham. Open University Press
Bybee R. W. 2015. The BSCS 5E instructional model and
21st century skills. Retrieved from
http://sites.nationalacademies.org/cs/groups/dbassesite/d
ocuments/webpage/dbasse_073327.pdf
Cápay M. , Klimová N., Engage Your Students via Physical
Computing! EDUCON 2019. In press.
Chen J. A., Pajares F., 2010. Implicit theories of ability of
Grade 6 science students: Relation to epistemological
beliefs and academic motivation and achievement in
science. Contemporary Educational Psychology,
Vol.35(1).
DesPortes K., Anupam A., Pathak N, and DiSalvo B. 2016.
BitBlox: A Redesign of the Breadboard. In Proceedings
of the The 15th International Conference on Interaction
Design and Children. ACM, 255–261.
Edwards S. H. 2004. Using software testing to move
students from trial-and-error to reflection-in-action.
ACM SIGCSE Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 1, 2004.
Feyzioğlu E. Y., Ergin Ö. The Effect of 5E Learning Model
on Seventh Grade Students’ Approaches to Learning.
Necatibey Faculty of Education, Electronic Journal of
Science and Mathematics Education, 01 June 2012,
Vol.6(1).
Foley, G. 1999. Understanding Adult Education and
Training. Second Edition. Sydney: Allen & Unwin,
225-239.
Fredricks J. A., 2014. Eight Myths of Student
Disengagement: Creating Classrooms of Deep
Learning. Los Angeles: Corwin.
Guthrie K., Jones T. B. 2012. Teaching and Learning: Using
Experiential Learning and Reflection for Leadership
Education. New directions for student services, 53-63.
2012.
Hodges S., J. Scott, S. Sentance, C. Miller, N. Villar, S.
Schwiderski-Grosche, K. Hammil, and S. Johnston.
.NET Gadgeteer: a new platform for K-12 computer
science education. In Proceedings of the 44th ACM
technical symposium on Computer science education,
pages 391–396. ACM, 2013
Jin K. H., Haynie K. and Kearns G., “Teaching Elementary
Students Programming in a Physical Computing
Classroom”. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual
Conference on Information Technology Education
(SIGITE '16). ACM, 2016, New York, NY, USA, 85-
90.
Kafai Y. B, Lee E., Searle K., Fields D., Kaplan E., and Lui
D.. 2014. A crafts-oriented approach to computing in
high school: Introducing computational concepts,
practices, and perspectives with electronic textiles.
ACM Transactions on Computing Education (TOCE)
14, 1 (2014), 1
Kaloti-Hallak F., Armoni M. and Moti Ben-Ari M. 2015.
Students’ attitudes and motivation during robotics
activities. In Proceedings of the Workshop in Primary
and Secondary Computing Education. ACM, 102–110.
Kolb D. 1984. Experiential learning. NJ: Prentice-Hall,
Englewood Cliffs.
Learning Theories. Discovery learning (Bruner) . [online]
Available at https://www.learning-theories.com/
discovery-learning-bruner.html
Lovászová G., Cápay M., Micheličková V. 2016. Learning
Activities Mediated by Mobile Technology : Best
Practices for Informatics Education. In: CSEDU 2016.
p. 394-401.
Moreno-Leon, J., Robles, G. Code to learn with Scratch? A
systematic literature review (2016) IEEE Global
Engineering Education Conference, EDUCON, pp. 150-
156.
Rubio M. A., Romero-Zaliz R.,Ma˜noso C., and A. P. de
Madrid. Closing the gender gap in an introductory
programming course. Computers and Education,
82(C):409–420, 2015.
Saito D., Washizaki H., Fukazawa Y.A. 2015 Comparison
of Programming Way: Illustration-based Programming
and Text-based Programming. In Proceedings of 2015
IEEE International Conference on Teaching,
Assessment and Learning for Engineering.
Schlechty P. C. 2001. Shaking up the schoolhouse. San
Fransisco, USA: Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Sentence S., J., Waite J, Hodges S, MacLeod E, Yeomans
LE. "Creating Cool Stuff" - Pupils' experience of the
BBC micro:bit. In Proceedings of the 48th ACM
Technical Symposium on Computer Science Education:
SIGCSE 2017.
Skalka J., Dlík M.. Conceptual Framework of
Microlearning-Based Training Mobile Application for
Improving Programming Skills. IMCL 2017 : 11th
International Conference on Interactive Mobile
Communication Technologies and Learning
Statter D., Armoni M. 2016. Teaching abstract thinking in
introduction to computer science for 7th graders. ACM
International Conference Proceeding Series, pp.80-83.
Voštinár P., Horváthová D., Klimová N. (2018) The
Programmable Drone for STEM Education. In: ICEC
2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11112.
Willems C., Jasper J., Meinel C. 2013Introducing Hands-On
Experience to a Massive Open Online Course on
openHPI. In IEEE International Conference on
Teaching, Assessment and Learning for Engineering
(TALE2013), pages 307–313.
Williams K. C., Williams, C. C. 2011. Five key
ingredients for improving student motivation.
Research in Higher Education Journal.
Zorn C., Wingrave C. A., Charbonneau E., LaViola Jr, J. J.
2013. Exploring Minecraft as a conduit for increasing
interest in programming, FDG, pp.352-359.
Zyngier D. 2008. (Re)conceptualising student engagement:
Doing education not doing time. Teaching and
Teacher Education, 24.
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
460
