
Effects of Physical Activity, Obesity and Smoking Habits on the Risk
of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Fauzie Rahman
1
, Dian Rosadi
2
, Mulyadi
3
, Andini Octaviana Putri
4
1
Department Of Health Policy and Management, Lambung Mangkurat University, Banjarmasin, Indonesia
2
Department of Epidemiology Departement, Lambung Mangkurat University, Banjarmasin, Indonesia
3
Student in Health Policy Management, Lambung Mangkurat University, Banjarmasin, Indonesia
4
Department Of Maternal and Child Health, Lambung Mangkurat University,Banjarmasin, Indonesia
Keywords: Physical Activity, Obesity, Smoking, Type 2 DM
Abstract: Diabetes mellitus (DM) characterized by the occurrence of hyperglycemia and metabolism disorders
associated with deficiencies of insulin secretion. Based on Health Research (Riskesdas) 2013, the number of
DM cases in Banjar District was the highest in South Kalimantan. This study aims to analyze the correlation
of physical activity, obesity and smoking habits with type 2 DM incidence in the work area of Martapura
Public Health Center. This research is a quantitative research using a case-control design. The population is
people who are treated at Martapura Public Health Center from September until December 2017. The sample,
as many as 150 samples with 75 types 2 DM cases and 75 control subjects were included in this research. The
sample was taken by purposive sampling technique. Data were analyzed by univariate with frequency
distribution table and bivariate analysis by chi-square test. Incidence of Type 2 DM occurs in less physical
activity (64%), obesity (56%) and smoking habits (33,3%). Chi-Square test showed there was correlation
between physical activity (p=0,009;OR=2,523) obesity (p=0,003; OR=2,877) and smoking status (p=0,039;
OR=2,385) with type 2 DM incident. It is advisable to community and health workers from applying a healthy
life behaviour to prevent the incidence of type 2 DM
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease characterized by
the occurrence of hyperglycemia and metabolic
disorders that are associated with a lack of insulin
work and secretion [World Health Organization,
2015]. The global prevalence of DM in the
community (aged 20-79 years) in 2014 as many as
387 million people (8.3%) with cases of type 2 DM
were the most common cases (70%) [International
Diabetes Foundation, 2015]. Based on IDF data in
2014, Indonesia ranked fifth of DM patients in the
world, with an estimated 9 million people with a
prevalence of 1.1%. According to the results of the
Basic Health Research (Riskesdas) 2013, the
prevalence of DM in Indonesia was 2.1%. This
prevalence is higher than the prevalence in 2007,
which was 1.1% [Ministry of Health of Republic,
Indonesia, 2013].
Banjar District is one of the districts in South
Kalimantan. Based on the data from Riskesdas (2013)
the number of cases of DM in Banjar District was the
highest in South Kalimantan (3.8%) and above the
national prevalence (2.1%) [4]. Based on data from
the Banjar District Health Office in 2016 the highest
health centre with DM cases was Martapura health
centre, which was 1114 cases with the highest cases
in type 2 DM (566 cases). Monthly morbidity data at
Martapura
Public Health Center, Banjar Regency, showed that
cases of type 2 DM still high in the last three months
as many as 39 cases in October, 43 cases in November
and 34 cases in December 2016.
Sukmaningsih WR (2016) study found
OR=7.737 which means that someone who has low
physical activity has a risk of 8 times more likely to
experience the incidence of type 2 DM. In addition,
there is a relationship between obesity and the
incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (p = 0,000) then
there is a significant relationship between obesity and
the incidence of type 2 DM. Smoking habits can also
trigger the occurrence of type 2 DM. Sukmaningsih
WR (2016) states that someone who smokes has a risk
332
Rahman, F., Rosadi, D., Mulyadi, . and Octaviana Putri, A.
Effects of Physical Activity, Obesity and Smoking Habits on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
DOI: 10.5220/0010676200002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 332-335
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

of 2,538 times more likely to experience the incidence
of type 2 DM.
Based on the above problems, a study was
conducted to explain the risk factors for the incidence
of type 2 DM in the work area of Martapura Public
Health Center, Banjar District
2 METHODS
This study used an observational analytic design with
a case-control design that aimed to analyze the
relationship between physical activity, obesity and
smoking habits with the incidence of type 2 DM in
the work area of Martapura Public Health Center. The
study population was all resident who seeks treatment
Martapura Public Health Centres many as 82,194
people in 2016. The number of samples was 150 with
75 cases samples (type 2 DM patients) and 75 control
samples (not type 2 DM patients). Determination of
samples using a purposive sampling technique. The
instrument used in this study was a questionnaire. The
independent variables in this study were physical
activity, obesity, and smoking habits, while the
dependent variable was the incidence of type 2 DM.
Data were extracted from the questionnaire into
Microsoft Excel and to SPSS 21.0 for analysis. Data
were analyzed using univariate frequency distribution
tables and bivariate analysis using the chi-square test.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Univariate Analysis
Based on the results of the study, the frequency
distribution of the research variables can be seen in
Table 1 below:
Table 1: Frequency Distribution of Research Variables.
Variable
Type 2 DM Incident
Case Control
n % n%
Physical
Activit
y
Less
Goo
d
48
27
64,0
36,0
31
44
41,3
58,7
Obesit
y
Obesity
Not Obesit
y
42
33
56,0
44,0
23
52
30,7
69,3
Smokin
g
Habits
Smoke
r
25 33,3 13 17,3
Non Smoke
r
50 66,7 62 82,7
Based on table 1, it is known that the majority
of respondents have a less physical activity that is
equal to 79 people (52.7%) compared to respondents
with good physical activity, which is equal to 71
people (47.3%). Physical activity will cause
metabolic changes that are also influenced by
duration, the weight of exercise and fitness level.
Proper physical activity can provide freshness of the
body, more controlled blood glucose, reduce the need
for drugs or insulin and can prevent type 2 DM
[Sugiyanto Z, 2014].
Based on table 1, it is known that 65 respondents
(43.3%) were obese, and 85 respondents (56.7%)
were not obese. Obesity is a direct factor that can
affect the incidence of type 2 diabetes, obese people
have excessive fat distribution in the body, especially
the abdomen is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes
[Trisnawati et all, 2013].
Table 1 shows that 65 respondents (43.3%) were
smokers and 85 respondents (56.7%) were non-
smokers. The biological habit of smoking can
increase free radicals in the body which causes
damage to endothelial cell function and damage beta
cells in the pancreas. It is known that the hormone
insulin is produced by beta cells in the pancreas, if
there is damage to the pancreas, it will affect the
production of insulin which will inhibit the entry of
glucose into the cell and eventually will increase
glucose levels in the blood and cause the incidence of
type 2 DM [Adiningsih et all, 2014].
3.2 Bivariate Analysis
Bivariate analysis was done to see the correlation of
each independent variable with dependent. The
results of the bivariate analysis can be seen in Table
2 below.
Table 2: Correlation between Independent Variables With
The Incidence Of Type 2 DM.
Varia
ble
Type 2 DM
Incident
p-
val
ue
OR
Case Control
n % n % (95% Cl)
Physi
cal
Activi
ty
Less
Good
4
8
2
7
64,
0
36,
0
3
1
4
4
41,
3
58,
7
0,0
09
2
,
5
2
3
(1,306 –
4,874)
Obesity
Effects of Physical Activity, Obesity and Smoking Habits on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
333
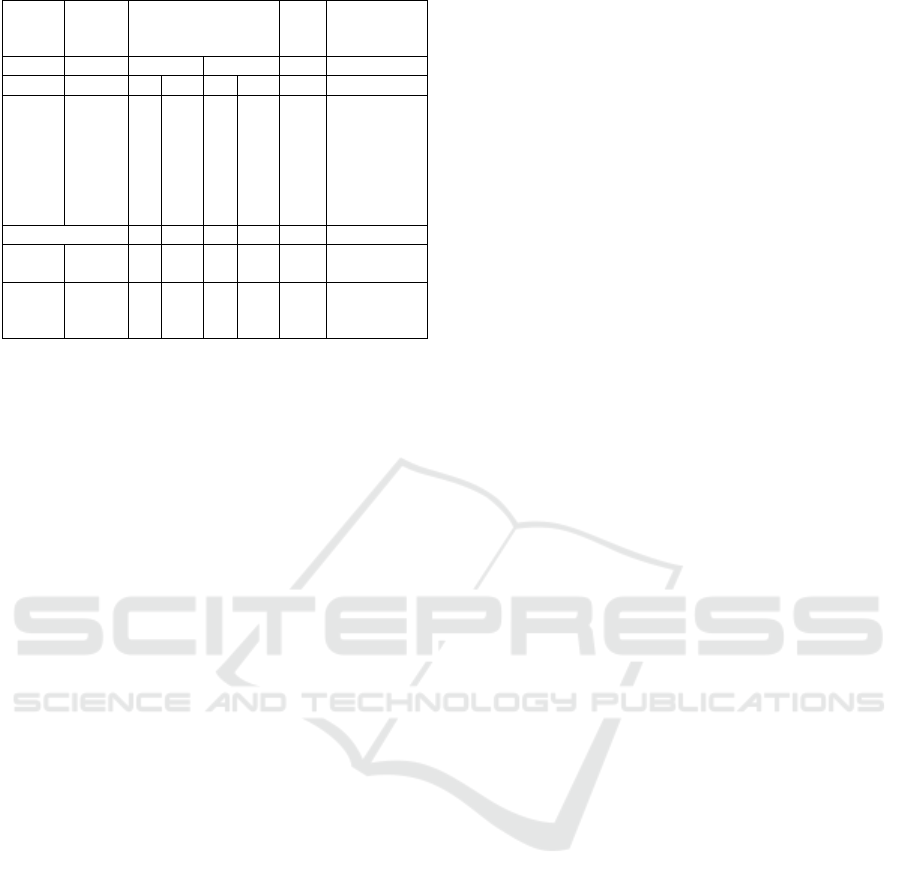
Varia
ble
Type 2 DM
Incident
p-
val
ue
OR
Case Control
n % n % (95% Cl)
Obesit
y
Non
Obesit
yy
4
2
3
3
56,
0
44,
0
2
3
5
2
30,
7
69,
3
0,0
03
2
,
8
7
7
(1,473 –
5,623)
Smoking Habits
Smok
e
r
2
5
33,
3
1
3
17,
3
0,0
39
2,385
Non
Smok
e
r
5
0
66,
7
6
2
82,
7
(1,108 –
5,134)
Based on table 2, it is known that there is a
relationship between physical activity and the
incidence of type 2 DM (p = 0.009; OR = 2.523).
Respondents with less physical activity were 2.523
times more likely for developing type 2 diabetes
compared to people with good physical activity.
Obesity is also a risk factor for the incidence of type
2 diabetes mellitus. Based on table 2, it is known that
there is a relationship between smoking status and the
incidence of type 2 DM (p=0.039; OR=2.338).
Respondents who were smokers were 2,385 times
more likely to develop type 2 diabetes compared to
non-smokers.
Another factor that has a relationship with the
incidence of type 2 diabetes is the smoking status of
the respondents. The results showed that there was a
relationship between smoking status and the
incidence of type 2 DM (p=0.039; OR=2.338).
Respondents who were smokers were 2,385 times
more likely to develop type 2 diabetes compared to
non-smokers
4 DISCUSSION
Type 2 DM is a hyperglycemic disease due to cell
insensitivity to insulin. Insulin levels may decrease
slightly or be in the normal range. Insulin is still
produced by pancreatic beta cells, then type 2 DM is
considered as non-insulin DM. Based on table 2, it
can be seen that there is a correlation between
physical activity with the incidence of type 2 DM.
Based on observations in the field, type 2 DM patients
rarely carry out regular exercise activities for reasons
of being lazy to exercise, and they feel tired quickly.
This, of course, can lead to a lack of response to
insulin (insulin resistance) so that glucose cannot
enter the cell.
This study is in line with the research of
Sukmaningsih WR (2016), which states that a person
who has low physical activity is eight times more
likely to experience type 2 DM [10].
Fikasari’s (2012) study showed that there was a
relationship between physical activity and the
incidence of type 2 DM (p = 0.045 <0.05). Regular
physical activity can reduce the risk factors for type 2
DM because physical activity can reduce weight and
improve sensitivity to insulin, which can improve
glucose control in the blood [Sukmaningsih, 2016].
The results showed that there was a correlation
between obesity and the incidence of type 2 DM.
Based on the results of the study, DM patient with
obese stated that their weight was high because they
did not maintain their diet and didn’t do a regular
exercise. This makes insulin unable to work optimally
to help body cells absorb glucose because it is
disturbed by complications of obesity, such as high
blood fat levels (cholesterol).
The results of this study are in line with the
research conducted by Jin Ook Chung, Dong Hyeok
Cho, Dong Jin Chung, and Min Young Chung (2012)
which states that there is a significant relationship
between obesity and insulin resistance (p <0.05).
Obesity condition causes excess fat deposits.
Freeform fatty acids can circulate in blood vessels
throughout the body and cause oxidative stress which
we are familiar with lipotoxicity. Lipotoxicity will
interfere with insulin receptor function [Jin OC et all,
2012].
The results of the statistics analysis showed that
there was a correlation between smoking habits with
the incidence of type 2 DM. Based on the facts in the
field, they smoke to eliminate tension and stress
because nicotine releases certain compounds to create
a calm and relaxing effect. Besides that they smoke
because they see the habits of their parents, who are
also smokers. This situation certainly causes insulin
resistance and causes blood sugar levels to increase,
which causes type 2 DM disease.
The results of this study are in accordance with the
research of Trisnawati et al. (2013) which states that
there is an influence of smoking habits on the
incidence of type 2 DM (p=0.002). Someone who
smokes 2.4 times more likely to developing type 2
DM compared to non-smokers. According to
previous research, smoking habits caused impaired
glucose metabolism and increased insulin resistance
which causes an increased risk of developing DM.
This result is in accordance with the Coronary Artery
Risk Development in Young Adults study data, which
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
334

found that active smoker was associated with the risk
of glucose intolerance.
Based on the theory, cigarettes are the main
product of tobacco-containing TAR, including the
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compound,
containing nicotine CO, HCN, and benzopyrene.
Nicotine can cause a reduction in sensitivity and
increase the occurrence of insulin resistance. In
addition, smoking can reduce HDL cholesterol in the
bloodstream; smoking can also make blood quickly
freeze, which increases the likelihood of arterial
blockage. Nicotine can increase blood glucose levels
which can cause insulin resistance. Nicotine
significantly affects the stress hormone cortisol. This
cortisol hormone causes the body to be resistant to
insulin
5 CONCLUSION
There was a correlation between physical activity,
obesity, and smoking habit with type 2 DM incident
in the work area of Martapura Public Health Center.
It is advisable to community and health workers from
applying a healthy life behaviour to prevent the
incidence of type 2 DM
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I am highly thankful to Martapura Subdistrict,
Martapura Public Health Center, all research
respondents and all the people who have helped this
research
REFERENCES
Adiningsih, Roro U. Factors Associated With The
Incidence Of Type 2 DM Ini Adults In Padang Panjang
City. Undergraduate Thesis. Padang: Public Health
Faculty Andalas University University, 2014
Ario, MD. Effect Of Nicotine In Cigarette For Type 2
Diabetes Mellitus. J Majority 2014; 3 (7): 75-80.
Fikasari Y. The Relationship Between Lifestyle And Patient
Knowledge About Diabetes Mellitus With The
Incidence Of Type 2 DM In DR Moewardi General
Hospital. Undergraduate Thesis. Surakarta:
Muhammadiyah University Surakarta, 2012
Health Office Of Banjar District. Dinkes Kabupaten
Banjar. 2016. Non Communicable Disease Data 2016.
Banjar District
International Diabetes Federation (IDF). IDF Diabetes
Atlas. 2015: 7.
Jin Ook Chung, Et Al. Associations Among Body Mass
Index, Insulin Resistance, And Pancreatic Β-Cell
Function In Korean Patients With New-Onset Type 2
Diabetes. 2012.
Ministry Of Health Of Republic Indonesia. Basic Health
Research: The Principal Results Of Riskesdas In Figure
Of South Kalimantan Province 2013. 2013. Jakarta:
Ministry Of Health Of Republic of Indonesia
Restylane NF. Diabetes Mellitus Type II. J Majority 2015;
4(5): 93-101
Sugiyanto Z. Risk Factors Associated With The Incidence
Of Diabetes Mellitus In Tugurejo Hospital Semarang.
2014. Research Paper. Semarang: Diponegoro
University
Sukmaningsih WR. 2016. Risk Factors Of Type 2 DM
Incidents In Puskesmas Purwodiningratan Work Area
Surakarta. Undergraduated Thesis. Surakarta:
Muhammadiyah University Surakarta.
Trisnawati S, Widarsa T, Suastikak. Risk Factors Of Type
2 Diabetes Mellitus In Outpatients In South Denpasar
District. Public Health And Preventive Medicine
Archive 2013; 1 (1):1-8.
World Health Organization (WHO). Global Report On
Diabetes, 2015. Global Burden Of Diabetes. France,
2015: 20.
Effects of Physical Activity, Obesity and Smoking Habits on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
335
