
Evaluation of Transportation Efficiency in Guangdong Province
Based on Data Envelopment Analysis
Yingxia Ye
He Yuan Polytechnic, He Yuan, Guangdong, China
email: yeyingxia0762@163.com
Key words: DEA, Transportation, Transport efficiency.
Abstract: Build the BCC model of evaluation of Guangdong province transportation operation efficiency based on the Data
Envelopment Analysis(DEA )method. Select operational mileages of all kinds of transport mode as input
indicators, passenger and freight turnover as output index. DEAP2.1 software used transport industry data of
Guangdong province for quantitative analysis and evaluation, the evaluation results show that before 2012, the
transportation efficiency of Guangdong province in the DEA is invalid, and return to scale is in an increasing
stage. Guangdong should increase the scale of transportation investment. Since 2012, Guangdong province's
transport efficiency has been effective in DEA,, and various modes of transportation have maintained overall
dynamic coordination.
1 INTRODUCTION
Transportation is one of the important infrastructure
and pillar industries in the national economic
structure. Guangdong province is located in the
south of the mainland of China. Guangdong
province is bordered by south of China sea, and
adjacent to Hong Kong and Macao, whichis an
important outlet of our country and the south gate,
with important traffic location and strategic position.
Since the reforming and opening up, the rapid
development of Guangdong's transportation industry
has provided a strong guarantee for the social and
economic development and promoted the
development of integrated transportation, modern
logistics and foreign trade. In 2016, the mileage of
new expressways in Guangdong province was 655
kilometers and the mileage of railway operation was
134 kilometers. The main bridge project of Hong
Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge is connected to the
whole line, and the new construction of the main
road of Jiangxi, Shenzhen and other major highways.
After the 13th five-year plan, Guangdong province
will become an increasingly important strategic hub
for the belt and road and the maritime silk road,
which will play a major role in promoting the
maritime logistics channel, the maritime silk road air
corridor, the opening of the silk road economic belt
and the two-way railway freight corridor.
Guangdong railway, aviation and other
transportation means made great progress and
outstanding achievements, but there are also some
problems, so the reasonable transportation efficiency
evaluation to the economy of the whole
transportation industry development is of great
practical significance. In this paper, Data
Envelopment Analysis (DEA) method is used to
analyze and evaluate the transportation efficiency of
Guangdong province from 2005 to 2015, and
calculate the relative effectiveness value of various
modes of transportation, analyze its development
and change characteristics and trends, thus providing
basis for regional strategy decision.
2 EVALUATION OF
TRANSPORTATION
EFFICIENCY IN
GUANGDONG PROVINCE
DEA is a multi-input and multi-output method based
on relative efficiency proposed by the famous
operational research scientist A.charnes and W.W.
Cooper in 1978. It is a non-parametric method to
evaluate whether the Decision making unit (DMU)
with multiple input and output is relatively effective.
It considers each evaluation unit as a DMU, and all
DMU constitute an evaluation group.
Ye, Y.
Evaluation of Transportation Efficiency in Guangdong Province Based on Data Envelopment Analysis.
In 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation (ICECTT 2018), pages 379-382
ISBN: 978-989-758-312-4
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
379
2.1 The BCC model of DEA evaluation
There are many methods of DEA model, and there
are two main types: fixed returns to scale DEA
model -- CCR model and variable returns to scale
DEA model -- BCC model. The CCR model is the
basic DEA model, which assumes that the input of
decision unit (DMU) can increase the output. That's
an ideal assumption. In reality, changes in scale lead
to different outputs. Therefore, a variable scale
compensation DEA model, namely the BCC model,
is produced. It measures the pure technical
efficiency, comprehensive efficiency and scale
efficiency of the decision unit. In this paper, the
BCC model is used to evaluate the transportation
efficiency of Guangdong province.
2.2 Input and output index selection
For transportation, the input indicators can include
the number of employees, the length of the line, the
number of stations, and the number of vehicles. The
output indicator can include passenger and freight
volume, and turnover, etc. Taking into account data
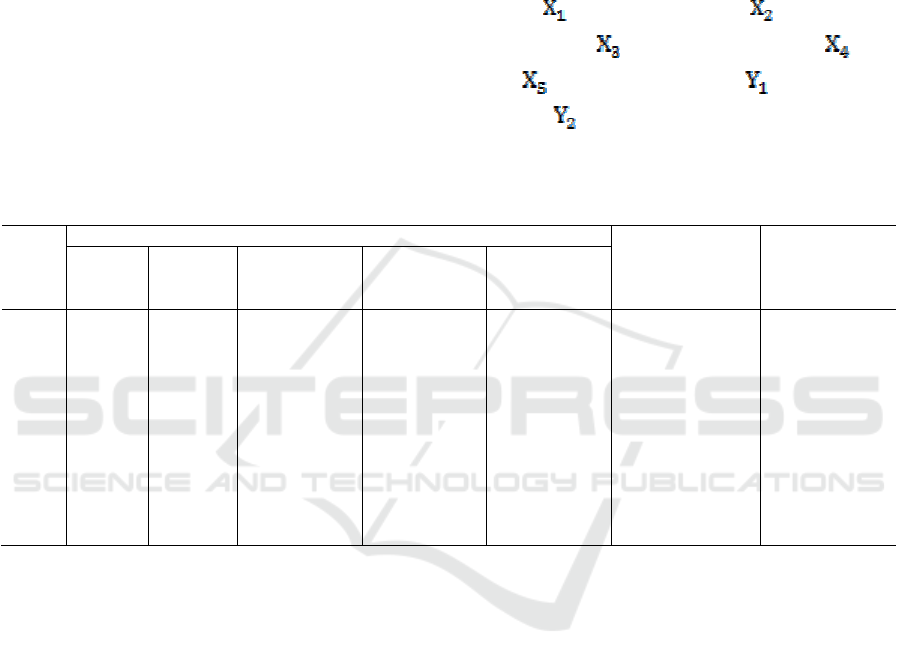
availability, the following index is used as input X
and output Y index (input indicator: railway line
mileage
; Highway mileage ; Mileage of
highway lines
; Water route mileage ; Air
miles
; Turnover of goods ; Turnover of
passenger
. The original data were obtained by
referring to the statistical yearbook of Guangdong
province from 2005 to 2015, as shown in table 1.
Table 1 The data of the input and output index of transportation in Guangdong province from 2005 to 2015.
Year
Mileage of the line Turnover of
goods
Turnover of
passenge
Railway
Highway
Expressway
Inland
waterway
Civil air route
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
1924
1862
1871
1859
2176
2297
2555
2577
3203
3818
5141
115337
178387
182005
183155
184960
190144
190724
194943
202915
212094
216023
3140
3340
3518
3823
4035
4839
5049
5524
5703
6266
7021
13596
13596
13596
13596
13596
13596
13596
13780
12096
12150
12150
1080706
1113479
1413918
1365418
1699629
1807385
1671100
1851000
2140600
2285800
2372900
3917.43
4162.77
4489.69
4591.22
4942.83
5933.88
7113.29
9780.56
12212.56
15020.92
15130.59
2043.23
2245.37
2626.71
2551.92
2853.30
3342.23
3851.84
4372.06
3538.10
3967.28
4335.79
Note: the mileage unit is km, and the freight
units are 100 million tons of kilometers, and the
passenger turnover units are 100 million people of
kilometers
In this case, because the civil aviation routes in
the statistical yearbook of 2011-2015 are
10,000kilometers, this article can only be converted
directly to kilometers.
According to the 11 decision units in table 1,
BCC model and DEAP2.1 analysis software were
applied to analyze the traffic efficiency of
Guangdong province. The evaluation results are
shown in table 2 and table 3 respectively.
As we can see from table 2, the transportation
system of Guangdong province from 2005 to 2015
has three years (2012, 2014, 2015) comprehensive
efficiency, technical efficiency and scale efficiency
are all effective in DEA. In the year when the DEA
was invalid, overall efficiency kept rising, and the
comprehensive efficiency reached the effective state
after 2012. In addition to 2009 and 2012, the
technical efficiency of transportation in Guangdong
province is 1, indicating that the optimization of
input and output has been achieved. At the same
time, the five years when DEA is invalid (2005,
2006, 2007, 2008, 2013), increasing return to scale
is increasing that is to say increase inputs can drive
the comprehensive efficiency of transportation.
Therefore, Guangdong province should increase the
transportation scale input, strengthen the
management of all links, and improve the
transportation efficiency.
ICECTT 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation
380
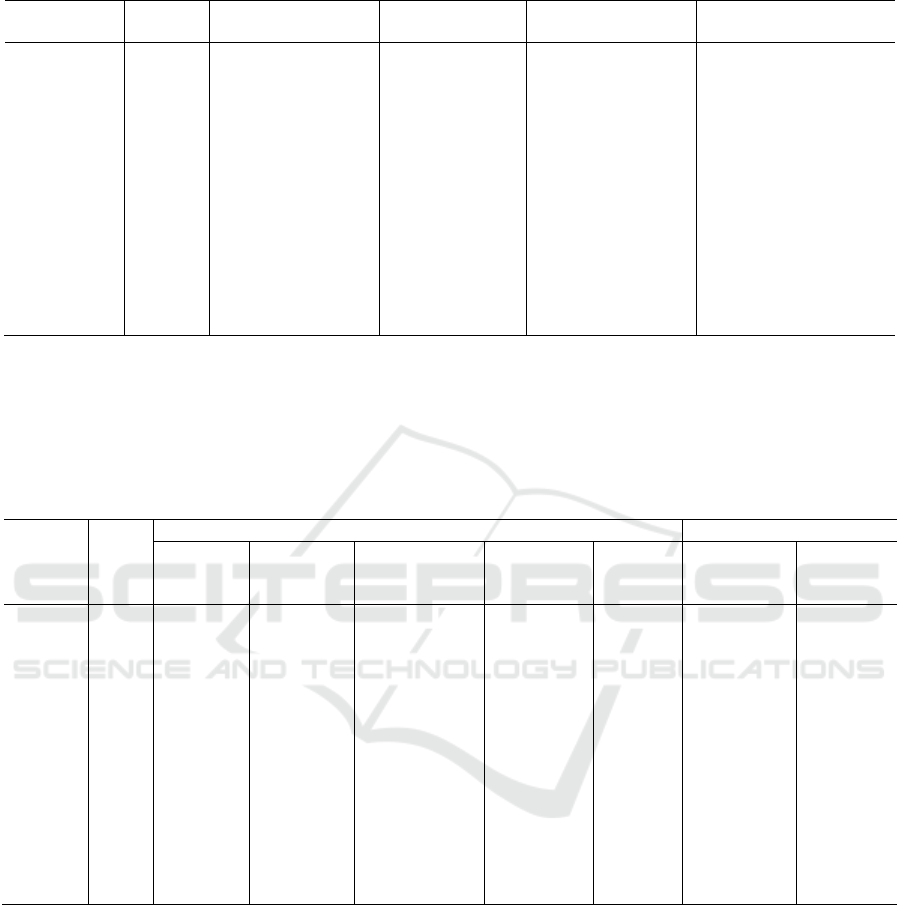
Table 2 Comprehensive efficiency, technical efficiency and scale efficiency of transportation.
DMU
Yea
r
Comprehensive
efficiency
Technical
efficiency
The scale efficiency Increase and decrease of
size
DMU1
DMU2
DMU3
DMU4
DMU5
DMU6
DMU7
DMU8
DMU9
DMU10
DMU11
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
0.822
0.854
0.943
0.843
0.893
0.873
0.976
1.000
0.974
1.000
1.000
1.000
1.000
1.000
1.000
0.984
0.992
1.000
1.000
1.000
1.000
1.000
0.822
0.854
0.943
0.843
0.908
0.880
0.976
1.000
0.974
1.000
1.000
Increasing
Increasing
Increasing
Increasing
Increasing
Increasing
Increasing
Constant
Increasing
Constant
Constant
As can be seen from table 3, there are years of
investment redundancy and insufficient output in
2009 and 2010. In 2010, redundancy and output
stood out. In 2010, the length of the railway was
319.776km of redundant expressways, 140880km of
air traffic and 132.6 billion tons of freight traffic.
Therefore, in 2009, Guangdong province should
appropriately reduce the operating mileage of
railway and the operating mileage of civil aviation
routes. In 2010, it should be appropriate to reduce
the mileage of expressway and the operating
mileage of civil aviation routes.
Table 3 Calculation results of traffic operation efficiency in Guangdong province.
DMU Year investment redundanc
y
insufficient out
p
ut
Railway Highway Expressway Inland
waterway
Civil air
route
Turnover
of goods
Turnover
of
p
assen
g
e
DMU1
DMU2
DMU3
DMU4
DMU5
DMU6
DMU7
DMU8
DMU9
DMU10
DMU11
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
13.306
319.776
137059
140880
1067
1326
3 CONCLUSION
Based on the model of variable return to scale DEA
model -- BCC model, this paper constructs an
evaluation of the operation efficiency of traffic
transportation in Guangdong province, and selects
the operating mileage of various modes of
transportation as the input index, and the passenger
and freight turnover as the output index, based on
the statistics of Guangdong province from 2005 to
2015, and evaluates the relative effectiveness of its
operation. Judging from the evaluation results,
Guangdong province has experienced a huge
increase in traffic mileage in recent years, and the
passenger and freight mileage has been significantly
improved. Although there are slight fluctuations in
the overall efficiency of transportation and
transportation, the overall trend of overall growth
has been maintained, and the effective value 1 is
finally reached. Except for individual years, the pure
technical efficiency is basically valid value 1. The
Evaluation of Transportation Efficiency in Guangdong Province Based on Data Envelopment Analysis
381

total compensation of scale is increasing, which
indicates that the transportation performance of
Guangdong province is generally good, and all
modes of transportation are in dynamic
coordination.
REFERENCES
cui yan, wu limei, qu jianhua, Assessment on Hennan
transportation efficiency based on DEA[J], henan
science, 2013,31 (2) : 201-204.
wang dongdong, li liqin, xiao liang, evaluation and
analysis of transportation efficiency in shaanxi
province based on DEA [J], practice and cognition of
mathematics, 2014,44 (10) :33-38.
Li Guishan, evaluation of highway transportation in Jilin
province based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation [D],
Jilin university, 2007.
Liu Jian, Ye Yingxia, application of DEA method in green
supply chain performance [J], industrial technology
economy, 2008, 27 (1): 63-65.
Charnes A, Cooper W W, Rhodes E. Messruing the
efficiency of decision making units[J]. European
Journal of Operational Analysis, 1996, 7: 99-101.
ICECTT 2018 - 3rd International Conference on Electromechanical Control Technology and Transportation
382
