
TAG INTERFACE FOR PERVASIVE COMPUTING
Paper Tag Interface using Imae Code
Dong-Chul Kim, Jong-Hoon Seo
Media System Laboratory, Dept. of Computer Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
Cheolho Cheong, Tack-Don Han
Media System Laboratory, Dept. of Computer Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
Keywords: 2D barcode, Image code, Tag interface, Pervasive computing, Ubiquitous computing.
Abstract: Recently, computing environments move to pervasive computing age with rapid growth of internet and
appearance of various mobile devices. This means computer offers more convenient life with linking
between physical object and digital information. With these advance of computing environment, several
researches are progress that are about tag interface to link between various physical objects and digital
information, which are image code like as barcode, or wireless technology based like as RFID. It leads high
expenses to read or write because RFID has to buy tags – as much as wanted – and has to need exclusive
hardware. But image code can be printed to paper and can decode from camera connected to computer, so it
is convenient and less maintenance cost. In this paper, we developed encoding and decoding algorithm for
image code and applied algorithm to the tag interface to access the information more easy and fast in
pervasive computing environment and develop.
1 INTRODUCTION
As the paradigm of computing evolves to pervasive
computing, physical objects and digital information
are being linked organically and life goes more
convenient. These changing affect not only
performance, but also user usability to more human-
friendly manner. By these evolution, it is more
important in pervasive computing environment that
linking naturally between physical space and digital
space with using tag interface. Tag interface
connects between digital information of virtual
space – which is in the computing environment or on
the network - and real objects in the physical world.
Many researches are in advance to progress
computing environment and to make more
intelligent with tag interface. There are so many
input devices - e.g. keyboard, mouse, character
recognition, etc - which digitalize physical
information. However, some drawbacks are exist,
e.g. many user effort, slow input speed, and high
error rate. Also, to digitalize huge information which
has complicated structure takes so many time and
frequent errors. [Kambayashi, 2001]. To overcome
these drawbacks, we proposed tag interface. Tag
interface is classified into RFID and image based
code. Image based code is used in various fields as
like barcode. Many services based on tag interface
use RFID instead of barcode. Because RFID tags
become more miniaturized, high effectiveness, and
less-expenses. However to construct these system, it
needs exclusive tags, readers, and writers, so initial
investment expenses are increased. Also, it is
difficult that user approach, and at cognition process,
many drawbacks exist - i.e. interferences, distance
recognition.
In this paper, we proposed paper tag interface
which uses image-based code to overcome
drawbacks of conventional RFID limited user
access, and expensive cost, and to diversify
application fields. At section 2, we survey tag
interface related conventional works, and section 3
shows proposed paper tag interface. At section 4, we
apply variety practical fields, and section 5
concludes the paper.
2 IMAGE CODE
Conventional image-based codes are divided into 1D
bar-code, and 2D image code. Firstly, 1D code is the
barcode that can be met in general. However, 2D
image codes are classified into Black-and-White
codes which use just two colors, and colourful code
356
Kim D., Seo J., Cheong C. and Han T. (2006).
TAG INTERFACE FOR PERVASIVE COMPUTING - Paper Tag Interface using Imae Code.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 356-359
DOI: 10.5220/0001572003560359
Copyright
c
SciTePress
- this code uses multiple colors to enhance the
capacity of the code in Table 1. The 1D bar-code is
used in several industries, with merit about fast
recognition and direction-free cognition ability. It is
most popular tag interface which is used in
circulation, logistics, etc. Also it has very high
recognition rate about 100%, and it can be printed
various place, i.e. paper, wrapping vinyl, etc, and
with inexpensive cost, and it can be diverse size. It
consists of white background and black lines which
has different thickness, and is recognized using CCD
or laser. Code system for barcode is supported in
EAN (European Article Number) which is
international standard and UPC code system.
However it has a defect that the size of the code
would be larger to represent a large size of data,
since the code has limited capacity and even lower
recording density. In 2D image codes, developed to
overcome a defect of 1D barcode - i.e. low capacity
and density, they have been developed widely, but
they have to be used with expensive and exclusive
readers only.
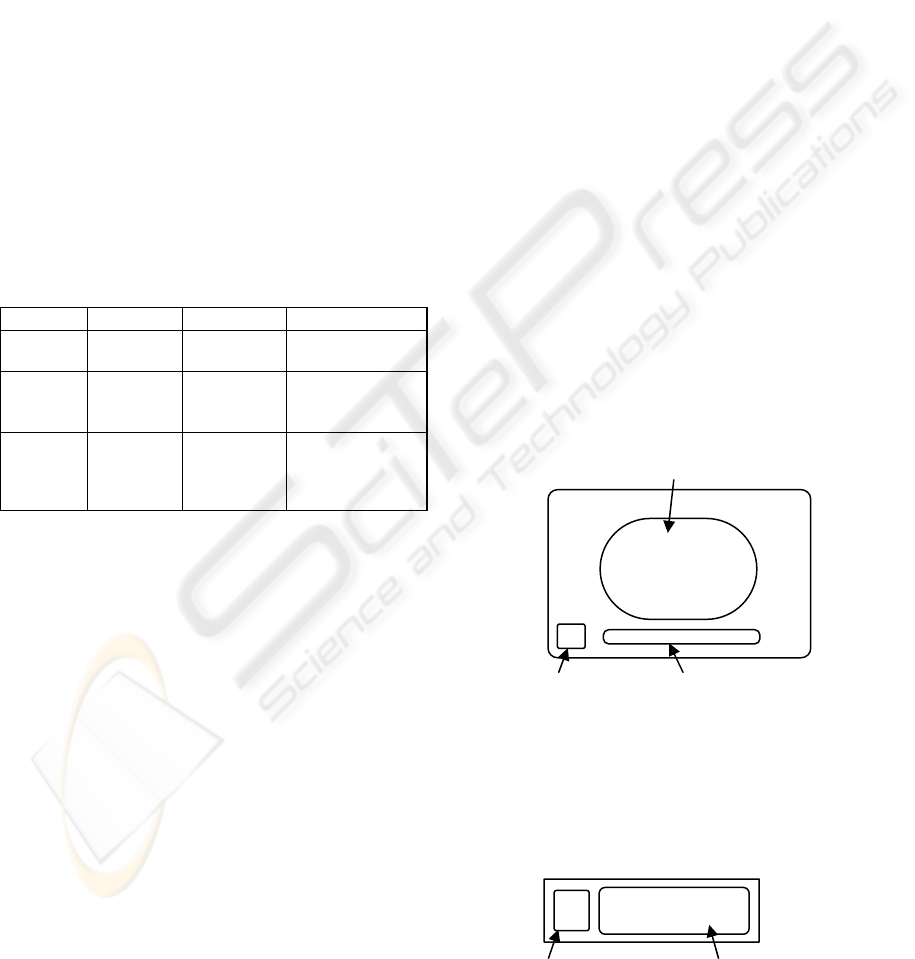
Table 1: Generation of image based code.
First Second Third
Code 1D Barcode 2D Barcode
2D Color Image
code
Keyword
Speed,
Correctiness
Capacity,
Speed, Error
Correction
Color, Mobility
Example
EAN/UPC,
Codabar, etc
QR code,
PDF417,
Data Matrix,
Maxi code, etc
ColorCode,
Ultracode, etc
Many codes have been developed for large
capacity and density. Denso have made QR code
which can be recognized quickly. Symbol
Technologies developed PDF 417 that has high
restoration rate[Pavlidis, 1992]. International Data
Matrix made the Data Matrix which can be made in
small size. UPS developed the Maxi Code to
separate postal matter in speedy. Sony made the
CyberCode for augmented reality. The Ultracode
from Zebra, the DataGlyphs from Xerox[Hecht,
2001], the ColorCode from ColorZip Media and so
many codes are developed, and these codes have
several advantages - e.g. data capability, data type
can be represented, recording density, etc - than 1D
barcode. Of these, the ColorCode and the Ultracode
use multiple colors and can store more data in same
size[Palmer, 1995]. In these semantics, 2D barcode
has portable data file and can be the data bridge
between computers they do not connected each
other[Want, 1999]. In other words, a data file printed
in 2D symbology from a computer system can re-
input to another system without keyboard.
3 PAPER TAG INTERFACE
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Paper tag interface system plays music when user
puts down a music tag on the guide line in front of
computer. When paper tag is put, the system
processes recognition algorithm from the inputted
camera image. That algorithm composed of
Binarization image, analysis component, and
detection candidate area of code. We decode image
code and recognize data if no error occurs from
candidate code area. We explain the structure of
image code and recognition process in 3.1. The
computer offers the user a service by performing
action – e.g. playing music, open internet browser,
etc – after tag recognition. In case of music tag, the
computer serves user through one of output devices
like as a speaker. We proposed two types of tags.
The one is card type and that’s size is 8.5 x 5.3 (cm)
in Fig. 1. Another is label type size of 5.5 x 1.5 (cm)
in Fig. 2. Label type is more portable than card type.
In case of card type, it has icon image in centre, Fig.
1-(1). The icon can help user recognize the purpose
of the tag. Bottom of the tag – Fig. 1-(2), there exist
image code for computer cognition and there is
additional information for user in Fig. 1-(3) – e.g.
the title, the singer, etc.
Figure 1: Paper Tag Structure of Card Type.
In case of label type, it has advantages of
portable and keeping. There is image code in Fig. 2-
(1) and additional information for user in Fig. 2-(2).
There are no icon image areas, because this type is
so small.
Figure 2: Paper Tag Structure of Label Type.
(1) Icon image area
(2) Image Code
(3) Additional Information
(1) Image Code
(2) Additional Information
TAG INTERFACE FOR PERVASIVE COMPUTING - Paper Tag Interface using Imae Code
357
User can generate tags easy as printing on paper.
Paper tag can contain some process of any action
and optional data or any file. If the data size is over
than image code capacity, then the data can be
uploaded server and image code has server address
and information of authentication.
3.1 Designing Image Code
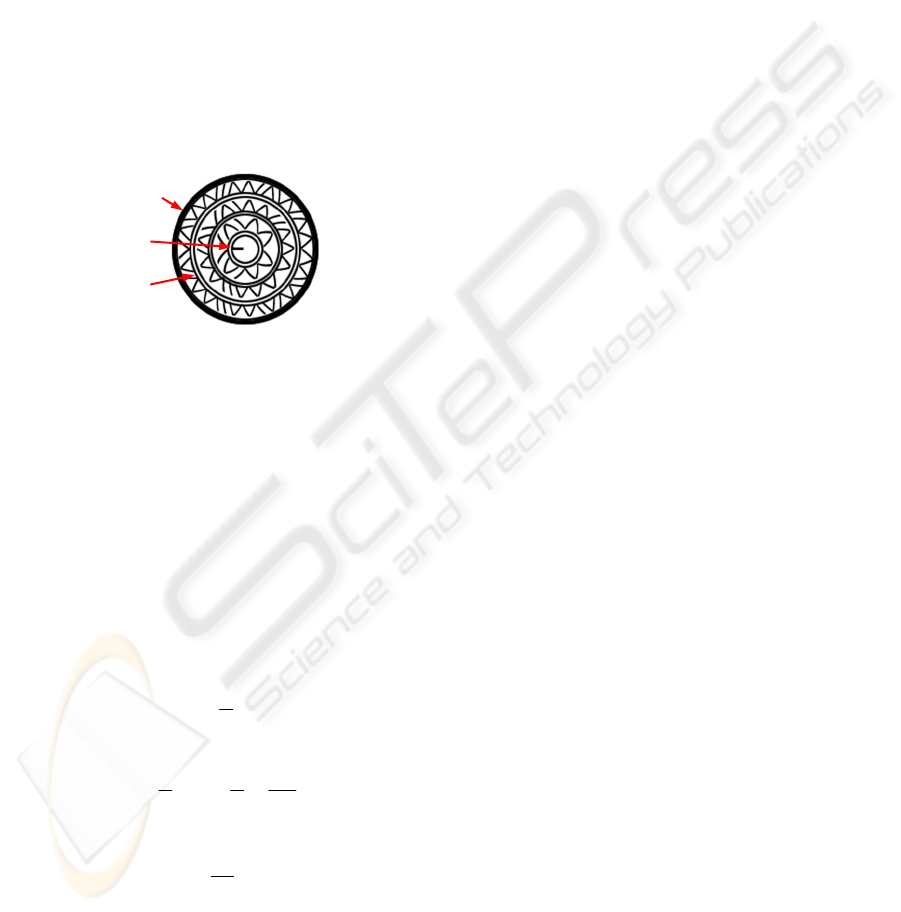
We design image code for paper tag interface.
Proposed image code is designed by circular strap
Fig. 3-(1). The centre of code has directional
indicator to inform the decoder the starting position
of this code, as like Fig. 3-(2). The circular strap is
formed data bits toward clockwise. Left 45 degree
and right 45 degree diagonal means '0' bit and '1' bit.
Reading data sequence ends at last data bits of k
th
-
layer.
Figure 3: Imae Code Structure.
If we let the index of circle at the code be 1, 2, …,
k from the most inner circle to the most outer circle,
the total capacity of data in the k
th
circle is
proportional to the circle index k. Let r
k
be the radius
of k
th
circle and n
k
be the number of codes in k
th
circle. Then we can say r
k
as
krr
k
=
(1)
And, we say θ
k
is a central angle of fan-shape
which a single pattern occupied. As the size of each
pattern is same, each pattern has uniform area and
all of patterns have fixed length of circumference.
kk
rl
θ
2
1
=
(2)
(1) is substituted for (2), then
k
kk
n
krrl
π
θ
2
2
1
2
1
==
(3)
Therefore the number of codes in the k
th
layer is,
k
l
r
n
k
π
=
(4)
As we can see above, we designed to proportion
the total number of patterns in k
th
circle with circle
index k.
3.2 Detecting Code Area and
Recognition Algorithm
The algorithm – for detecting code area and
recognition the code – can be briefly described as
following. At first, decoder pre-processes for
separating code area from the background image at
the inputted image. Filtering process filters
candidate areas. This process reduces operation
loads of decoding. After detection of code area,
decoder computes centre point. Decoder reads
circular data strap from the start bit that was found
by directional indicator, and recognize all of data
sequence after parity check. More detailed
description is explained as following 4 steps.
Step 1: Binarization
Decoder thresholds inputted original image, Fig.
4- (1), to binarized image, Fig. 4-(2) before
analysis image. Firstly, to find the value of
threshold, decoder converts original image to grey,
and calculates an average value from min-max
histogram. This process called “dynamic
binarization”, which provides more flexible
adaptation to various environment than fixed value
thresholding.
Step 2: Compnent Shape Analysis
Firstly, to get shape information as like Fig. 4-(3),
we apply laplacian mask to binarized image and get
contour which have connected component
information by tracking edge lines. By applying
laplacian mask, we can get good results and less
amount of computation loads to get edge. Especially,
it is easy to track contour information because
laplacian masking produces 1pixel edge result from
the binarized image.
Step 3: Candidate Filtering
We get the area which is estimated as code field,
with following two filters from the previous contour.
The first filter is the outline length information. We
use the outline information to remove the noise area.
If the length of the outline is too short, we would
estimate it as small object of background or noise, so
it would be estimated as the background. The second
filter is circular rate. We filtered out non-code areas
from the result of first filter with using circular rate.
We define circular rate e as following equation.
2
/4 lAre ×=
π
(5)
Above equation (5) is gained from the circular
area formula (
2
rA
π
=
) and circular circumference
formula (
2
2 rl
π
=
). The more the circular rate e is
near to 1.0, the more it can be estimated as a circular
Data
Strap(3)
Directional
Indicator(2)
Circular
Strap(1)
SIGMAP 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SIGNAL PROCESSING AND MULTIMEDIA
APPLICATIONS
358

shape and it would be decides as the final candidate
code area, Fig. 4-(4). We can decrease the
calculation quantity by filtering non-code area out.
Step 4: Decoding and Error Detection
We compute the center point and the radius from
the extracted candidate area, and look for the pattern
around the center point circularly. Firstly, we search
the indicating sign which is showing the start bit. To
start to read the data, we find the start bit from the
most outer layer in the direction of the indicating
sign. A bit pattern means 0 or 1 – inclined left(‘/’) is
0 and inclined right(‘/’) is 1. After decoding patterns
we apply error check algorithm to detect errors. If
there are no errors detected, it can be recognized as
correct codes, and then decoding process is regarded
as done.
(1) Original Image (2) Binarization
(3) Edge Extraction (4) Get Image code Area
Figure 4: Recognition through Preprocessing.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND APPLICATION
We organized 4 layers for test, and data is inserted
with ratio of 2:3:4 from the 2
nd
layer to 4
th
layer. We
tested the printed picture of the 2.5 × 2.5 (cm) size
code. We could save the data of 147bits in the used
test code if it except the parity code. The size of the
data would increase exponentially when more layers
appended. At above size, maximum layer can be
recognized are 7 and then more than 800 bits can be
contained. We experiment paper tag system as
following example. We applied the tags as a paper
storage media, security and verification keys,
multimedia educations system for children,
computer interface of easy approach, entertainments
interface (photo, music, move) for a media center
computer.
(1) File Case Tag (2) Paper Storage
(3) Music Tag (4) E-mail Tag
Figure 5: Paper Tag Applications.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have made up tag interface using
image code system architecture for easy accessing to
digital information in pervasive computing
environments. We design and apply image code in
this system. It can be possible that there are no needs
to hardware devices like RFID. User can use card
type or label type tag for their purpose. It is easier
and cheaper than RFID tag system to generate tags
by printing on paper and to decode by using PC
camera. We develop algorithm of encoding and
decoding for image code generation and recognition.
The following points are left as future problems.
Generation of paper tag with no use computer
system and increasing tag capacity.
REFERENCES
Kambayashi, Y., Tarumi, H., Morishita, K., 2001. Digital
Tags: Data with Restricted Accessibility for e
Commerce Applications, Australian Computer Science
Communications.
Pavlidis, T., Swartz, J., and Wang, Y. P., 1992.
Information Encoding with Two-Dimensional Bar
Codes, IEEE Computer Magazine.
Hecht, D.L., 2001. Printed embedded data graphical user
interfaces, IEEE Digital Object Identifier.
Palmer, R. C. 1995. The Bar Code Book, third edition,
Helmers Publishing.
Want, R., Fishkin, K.P., Gujar, A., Harrison, B.L., 1999.
Bridging Physical and Virtual Worlds with Electronic
Tags, Proc. of CHI’99.
TAG INTERFACE FOR PERVASIVE COMPUTING - Paper Tag Interface using Imae Code
359
