
LEVEL HASH TABLE RESOURCE DISCOVERY MECHANISM
IN GRID ENVIRONMENT
Liu Weidong, Song Jiaxing, Wang Yue
Department of Computer Science and Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Keywords: Level Hash Table, Resource Discovery, Grid Computing.
Abstract: Resource discovery is important in Grid. In this paper, a novel resource discovery mechanism based on
level hash table is presented. The Grid resources are hashed into keys, and each LHT Node stores keys that
could be mapped into resources registered on LHT Nodes of current sub-tree.We give the detail
implementation of it and the simulation results show it works efficiently.
1 INTRODUCTION
A basic service in grid is resource discovery: given a
description of resources desired, a resource
discovery mechanism returns a set of (contact
addresses of) resources that match the description.
Resource discovery in a grid is made challenging by
the potentially large number of resources and users
(perhaps millions) and considerable heterogeneity in
resource types and user requests(Ian, 2001).
Several research works have made their efforts
on resource discovery. Some of them used the
centralized architecture(Condor), and some used the
decentralized architecture. Their results show that a
decentralized approach is suited for resource
discovery in Grid environment.
Peer-to-peer systems and applications are
distributed systems without any centralized control
or hierarchical organization(Stoica, 2001). P2P
systems can be categorized as either unstructured or
structured networks. These systems provide failure
tolerant approaches to looking up the location of an
object (Min C., 2004).
The Gnutella (Clip2) P2P file sharing system
uses an unstructured network among peers, and each
query for an object location is flooded to the whole
network. But, recent studies show that this approach
does not scale well because of the large volume of
query messages generated by flooding.
On the other hand, structured P2P networks such
as those using distributed hash tables (DHT)
maintain a structured overlay network among peers
and use message routing instead of flooding. Recent
proposed DHT systems include Tapestry (Ben,
2001), Pastry(Antony, 2001), Chord (Stoica, 2001),
CAN(Ratnasamy, 2001) and Koorde(
Kaashoek,
2003). In these systems, objects are associated with
a key produced by hashing the object name. The
DHT nodes maintain an overlay network, with each
node having several other nodes as neighbors. When
a lookup (key) request is issued from one node, the
lookup message is routed through the overlay
network to the node responsible for the key.
Therefore, these DHT systems provide good
scalability as well as failure resilience.
Existing P2P location mechanisms focus on
specific data sharing environments and, therefore, on
specific requirements (Adriana, 2002). In Gnutella,
the emphasis is on easy sharing and fast file
retrieval, with no guarantees that files will always be
located. In contrast, systems such as CAN and
Chord guarantee that files are always located, while
accepting increased overhead of file insertion and
removal.
To gain good resource discovery performance in
Grid environment, we investigate a new LHT
mechanism on tree-based network architecture.
Instead of flooding mechanism, we employ a
purposeful routing mechanism based on hash
algorithm.
The rest of paper is organized as follows. Section
2 describes LHT mechanism, section 3 shows
simulation result; finally, section 4 concludes the
paper and gives the future works.
83
Weidong L., Jiaxing S. and Yue W. (2006).
LEVEL HASH TABLE RESOURCE DISCOVERY MECHANISM IN GRID ENVIRONMENT.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 83-87
DOI: 10.5220/0001426800830087
Copyright
c
SciTePress
2 LHT MECHANISM DESIGN
In general, LHT resource discovery mechanism uses
a hash-based keyword matching algorithm. We
assume that each resource has one attribute as its
identity, such as its name. So resource is associated
with a key produced, for instance, by hashing its
identity.
Due to the limited hash space, the resources with
different names may have the same key value, so,
there must be a certain quantity of resources with the
same hash key in our system, which is the point that
benefits our LHT mechanism design most.
So, based on LHT Mechanism, users could pick
up the resources - which meet their requirement -
from the result list. Or, we could deal with result list
further with other attributes to improve the Quality
of Service.
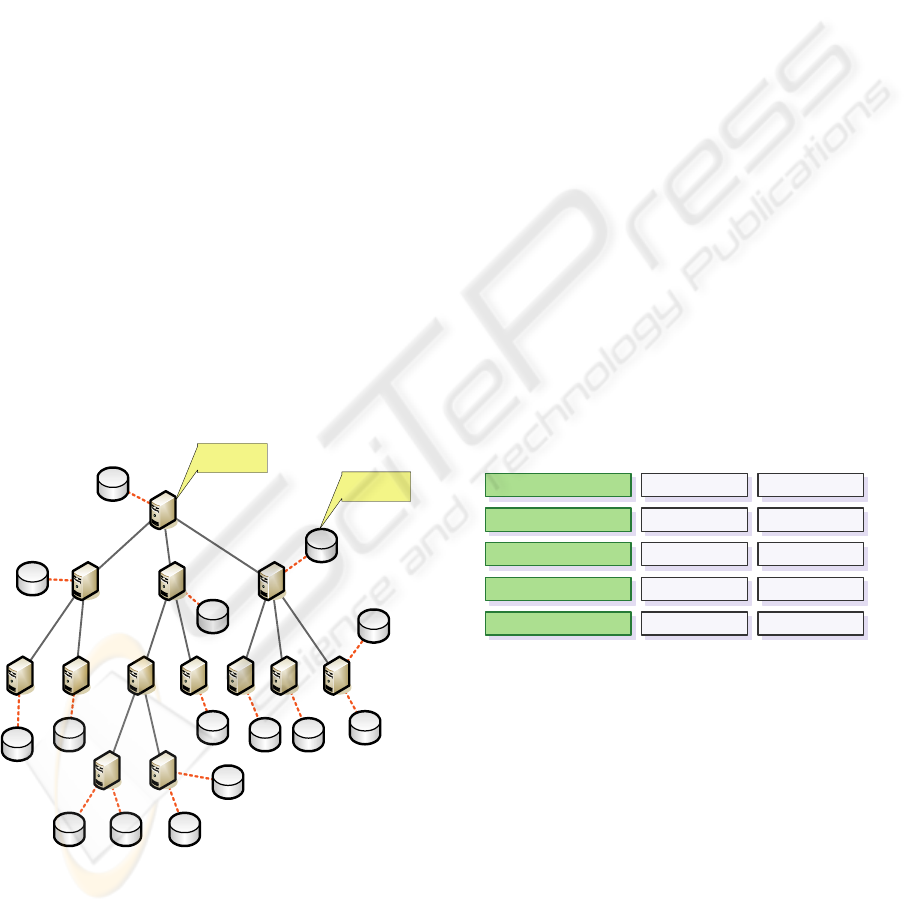
2.1 LHT Architecture
The network structure LHT mechanism runs on is
organized as a tree. That means an LHT Node has
only one parent node, and has several child nodes.
Before they can be discovered, they have to
register on an LHT Node. The resources from other
computers or devices, or from the node itself, can be
registered on the LHT Node. Each LHT Node in the
system is responsible for storing a certain range of
keys.
1
2 3 4
5 6 7 8 9 10 11
12 13
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 9 10
11
12
13 14
15
LHT Node
Resource
Figure 1: Architecture of LHT Mechanism.
That certain range of keys could be mapped to
the resources registered on it or on its child nodes.
Figure 1 shows the architecture of LHT mechanism.
The children number of one LHT Node is
limited in the system. But we can adjust it to adapt
dynamic factors, such as the whole number of LHT
Nodes, to maximize the performance. When a new
node wants to join the system, it would find the
nearest LHT Node and register as a child node.
Thus, the tree will tend to balance naturally, because
the nodes join the system from each place has the
same probability.
When a query is sent to a LHT Node, system will
compute the hash key and the searching process is
launched from the root to the right nodes. At last a
resources address list will be returned. This resource
discovery mechanism allows nodes to get resources
based on their key, thereby supporting the hash-
table-like interface.
2.2 Data Structures and Operations
Each LHT Node should maintain Resource Register
Table (RRT) and Resource Hash Table (RHT). And
when resource register event occurs, or new LHT
Node join the system, RHT must be transformed to a
new type of table - Resource Mapped Table (RMT) -
which will be sent to higher level LHT Nodes.
Now we will describe these data structures based
on LHT architecture shown in Figure 1. There are
two resources registered on LHT Node 12. Table 1
shows the Resource Register Table maintained by
LHT Node 12. Note that h(resource8) means the
hash key produced by the identity of Resource 8.
Table 1: Resource Register Table of LHT Node 12.
Resource Name
Resource Address
Resource Description
Other Attributes
Hash Key
Resource 8
h(resource8)
Location 8
Description 8
Attributes 8
Resource 9
h(resource9)
Location 9
Description 9
Attributes 9
Resource Register Table It stores detail of all
the resources registered on current node. In this
table, the resources are indexed by the hash key, so
that we can access the detail information of the
resources directly. The operations associated with
RRT are Resource Register Operation and Resource
Unregistered Operation.
Resource Hash Table It has two dimensions.
The columns are LHT Nodes list, including current
node and child nodes DIRECTLY UNDER current
node. The rows are keys list of the whole hash
space. RHT is shown in Table 2.
In Resource Hash Table, resources with the same
key will be organized in one row. The data of the
table could be designed as a bitmap. The Boolean
value of a cell shows that whether the resource with
ICE-B 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON E-BUSINESS
84
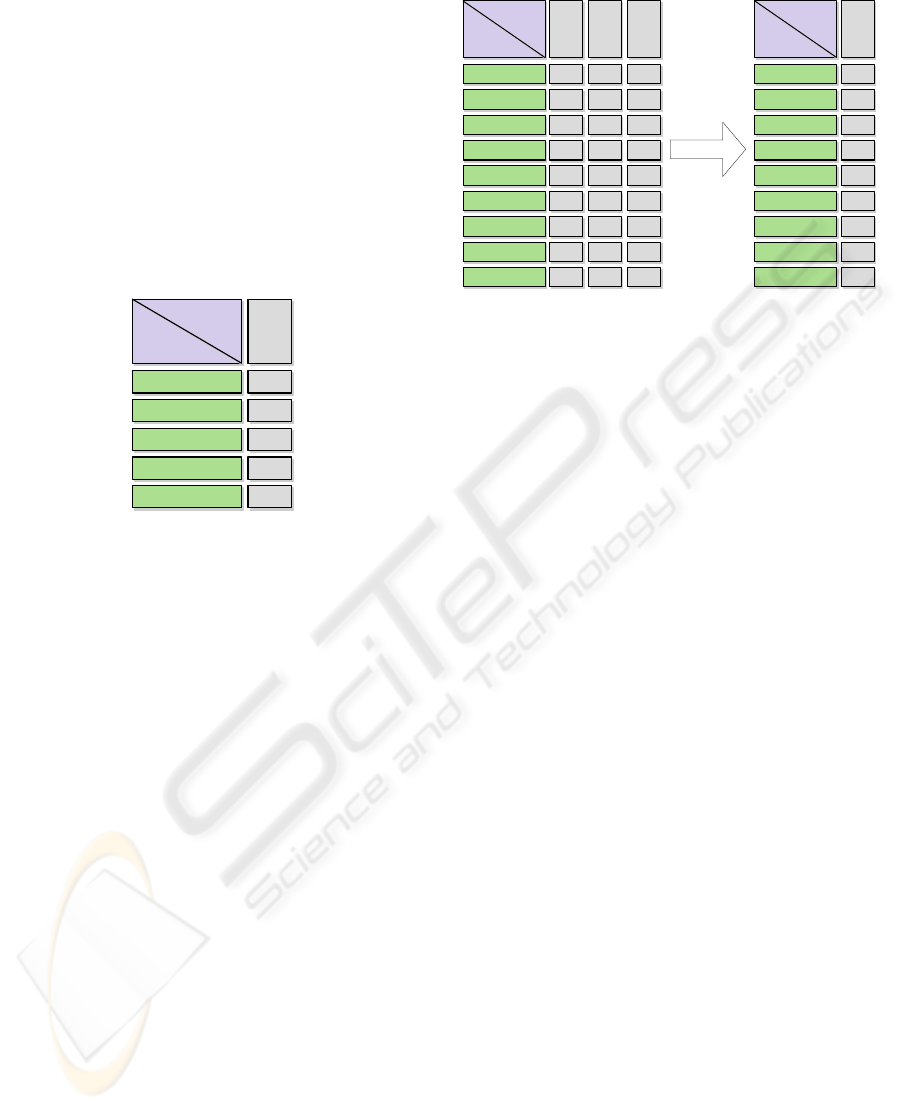
this hash key (row name) is registered/indexed on
that LHT Node (column name).
When the RRT is changed, that means new
resources register or some resources unregistered,
modification operations must be called. Insert
Modification Operation deals with new resources
register events. What we only should do is to modify
the local node column of the bitmap, change the
correspondence value to positive. On the contrary,
Delete Modification Operation will also modify the
local node column of the bitmap, and turn the
correspondence value to negative.
Table 2: Resource Hash Table of LHT Node 12.
LHT Node
Key Space
...
h(resource8)
...
h(resource9)
...
LHT
Node
12
...
1
...
1
...
Higher level LHT Node knows that the key
hashed by a certain resource could exist in which
sub-trees of its child nodes, so it can route the query
to the lower level LHT Nodes. When resource
register event occurs, or new LHT Node join the
system, RHT must be transformed to Resource
Mapped Table which will be sent to higher level
LHT Nodes.
Resource Mapped Table The structure of
Resource Mapped Table is same with RHT, but it
has only one column. Each cell value in RMT is the
result by computing logical OR operation among all
the cells value of the same row in RHT. In other
word, RMT shows which key can be found in
current node’s sub-tree, but ignores the resource
associate with the key is registered exactly on which
node of the sub-tree.
And when parent LHT Node receives the RMT
sent by its child nodes, it will merge it into its
Resource Hash Table. So the query can easily be
routed to lower level nodes. The purpose of design
takes the advantages of distributed system, and
avoids network traffic by flooding mechanism.
Table 3 shows the RHT of LHT Node 7, after
merging the RMT sent from LHT Node 12 and 13,
and also shows the RMT of LHT Node 7, which will
be sent to parent node.
Table 3: An example of Resource Hash Table.
LHT Node
Key Space
...
h(resource8)
...
h(resource9)
...
LHT
Node
7
...
0
...
0
...
h(resource10)
...
h(resource12)
...
0
...
0
...
LHT
Node
12
...
1
...
1
...
0
...
0
...
LHT
Node
13
...
0
...
0
...
1
...
1
...
LHT Node
Key Space
...
h(resource8)
...
h(resource9)
...
LHT
Node
7
...
1
...
1
...
h(resource10)
...
h(resource12)
...
1
...
1
...
transform
2.3 Resource Register Service
The resources must register on an LHT Nodeto jion
the Gird system. And when it is temporarily
unavailable, the owner of the resource can unregister
it, or the resource is unregistered by Grid Monitor
Service. So the Resource Register Service has to
provide a parameter which used in the request, to
determine whether the resource should be registered
or unregistered.
When Resource Register Service receives a
resource register request, the resource’s detail would
be added into the RRT of current LHT Node by
Resource Register Operation. Then Insert
Modification Operation should be called to modify
the local node column of RHT. Next, RMT is
generated from RHT and sent to parent node. Parent
node calls Update Merging Operation to modify its
RHT, and transforms to RMT sent to higher level
node.
Similarly, if the Resource Register Service
receives a resource unregistered request, the
operations have to be called are Resource
Unregistered Operation, Delete Modification
Operation on local node, and Update Merging
Operation on higher level nodes.
2.4 Resource Discovery Service
Resource Discovery Service is the key process of
LHT Mechanism. In our system, although the
resources are registered on distributed nodes, we do
not have to search for request resource by traversing
all nodes, and also do not need to search for request
resource on a centralized server with heavy load.
In LHT mechanism, once a requester submits his
resources requirement to an LHT Node, the
following processes will be launched.
The LHT Node received the original request
could be called Request Node. It must compute the
LEVEL HASH TABLE RESOURCE DISCOVERY MECHANISM IN GRID ENVIRONMENT
85
hash key of the request resource and send the
searching request with the key to root LHT Node.
When a LHT Node receives a request, it fetches
the row of its RHT which row name is that key.
Check the cells value in this row, if all the value is
negative, the request is dropped. Otherwise, pick the
columns whose cell value is positive. Now we find
all child nodes matching that key then the request
will be sent to them, then repeat 2). Certainly, if the
nodes we found contains current node itself, which
means resources with that key had been registered
on local node directly, we should check the RRT and
send a message with detail of this resource to
Request Node, and then go to 3).
Request Node returns resources list to the user.
Then user browses the resources description to see
whether there are resources he really wants. If there
is at least one resource he wants, the process of
resource discovery is finished.
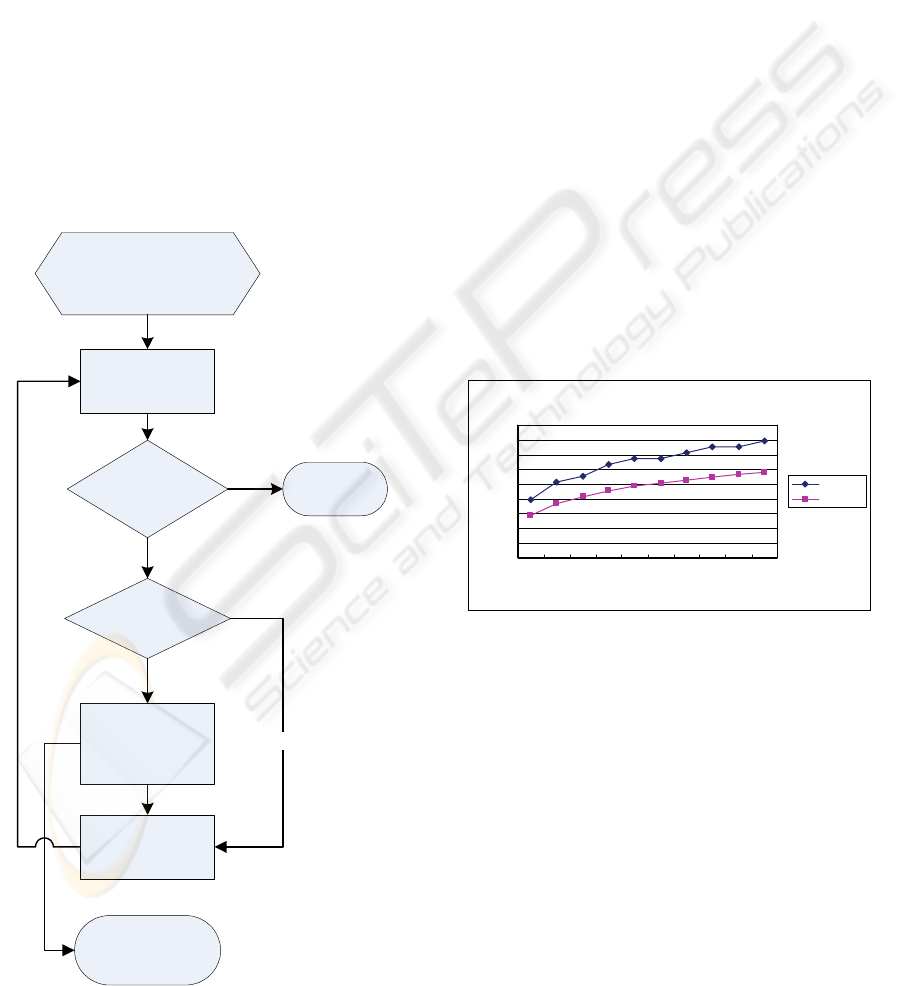
This process can be simply described as Figure
2.
Request Node receives
original request, then hash
key and send to root
Fetch
correspondence row
from RHT
All the value of the
row is negative
Y
Send request to
other child nodes
with positive value
N
Value of current
node is positive
Check RRT and
send description of
resource to Request
Node
Y
Return resources list
to user
N
Drop the
request
Figure 2: Chart discription of resource discovery.
3 PERFORMANCE ANALYSES
AND SIMULATION RESULTS
The simulation tool we used is GridSim toolkit
(Buyya, 2002). Above all, some variables should be
defined. The number of LHT Nodes in the system is
p, and the children number of one node is limited to
q. There are N resource exist in the system. The
space of hash algorithm is H.
a) Storage Space needed by one LHT Node.
RRT contains information of all the resources
registered on local LHT Node. On average, there are
N/p resources registered on a LHT Node.
RHT contains information of the mapping
relations between keys and child nodes. The row
number of RHT is the hash space H.
In one word, storage space is limited by system
variables and it won’t increase significantly along
with network size.
b) Resource Discovery Efficiency.
Obviously, LHT routing mechanism can
guarantee to finish discovery operation in O(log
q
p)
hops when the tree-based structure is close to
completely balanced. Now we assume the resources
have to be found at the leaf nodes of the tree. Figure
3 shows the relation between query latency and
network size.
Quer y Lat ency as a f unct i on of net wor k si ze
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Nu mber of LHT Nodes
Quer y Lat ency ( ms)
Maxi mum
Av e r ag e
Figure 3: Query latency.
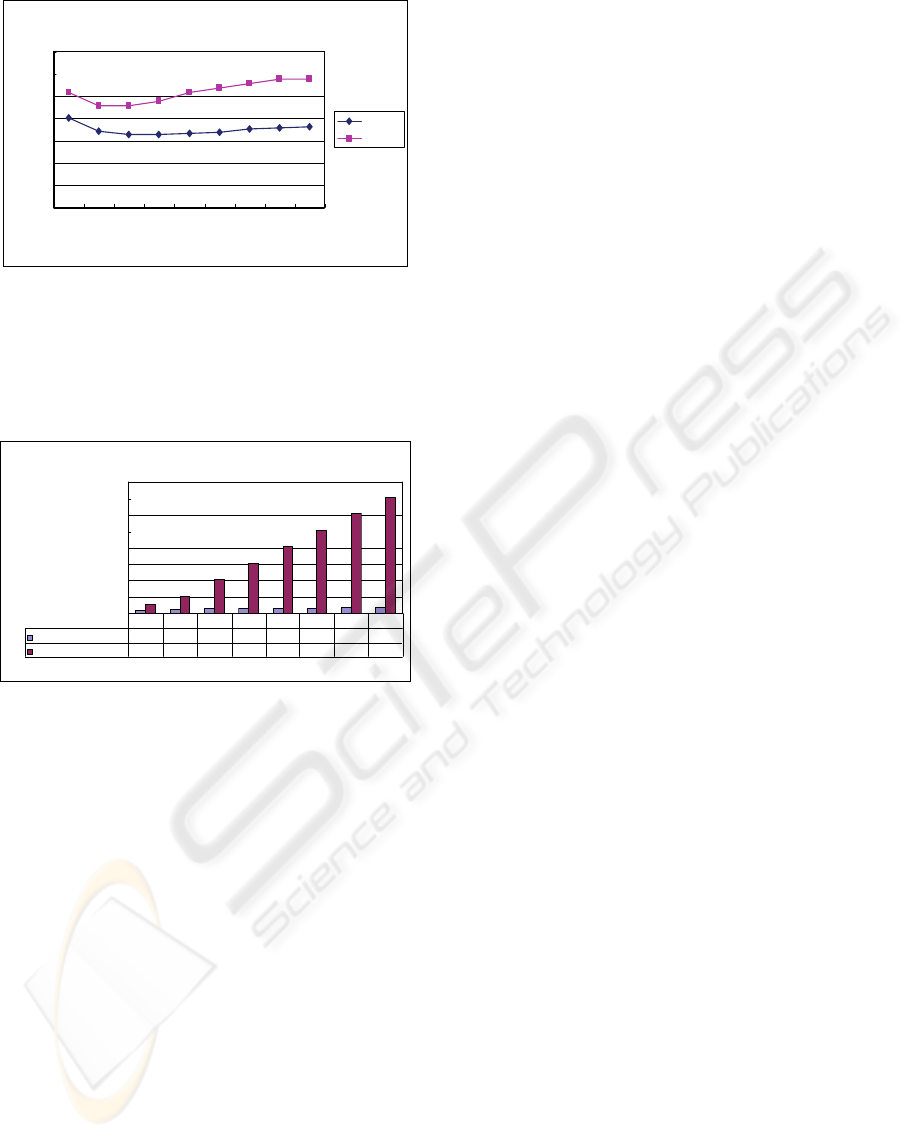
And the children number of nodes will also
influence the query performance. When the network
size is fixed, changing the children number properly
will improve the query latency. Figure 4 shows that
the relation between query latency and children
number of nodes.
ICE-B 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON E-BUSINESS
86
Quer
y
Lat enc
y
vs. Chi l dr en Number
(
500 LHT Nodes
)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
2345678910
Ch i l d r e n Nu mber of LHT Nodes
Quer
y
Latenc
y
(
ms
)
Aver age
Maxi mum
Figure 4: The relation between query latency and chinlren
number of nodes.
At last, we will demonstrate that LHT
Mechanism is superior to flooding mechanism. We
can see the simulation result in Figure 5.
Co mpar i son bet ween LHT Mechani sm and Fl oodi ng Mechani s
m
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
Nu mber of Nodes
Quer y Lat ency ( ms)
LHT Mechani sm
42. 589 49. 478 56. 309 60. 559 63. 317 65. 334 67. 865 68. 684
Fl oodi ng Mechani sm
112. 96
213
413. 02
613. 03
813. 03
1013
1213
1413
50 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
Figure 5: Comparison with flooding mechanism.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
In this paper, we introduce a LHT Resource
Discovery Mechanism. The performance analyses
and simulation results show that when network
topology is definite, LHT Mechanism can find
resources in certain hops. The results also tell us that
the change of network topology will influence the
resource discovery performance. The tree-based
structure is more balanced, and then the performance
will be better.
We are developing a prototype of LHT
Mechanism. In future, we will improve our
mechanism to provide multi-attributes resource
discovery, such as QoS parameters.
REFERENCES
Adriana I., 2002. Locating Data in (Small-World?) Peer-
to-Peer Scientific Collaborations. Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, Vol. 2429, p 232 – 241.
Antony R., 2001. Peter Druschel: Pastry Scalable,
Decentralized Object Location, and Routing for Large-
Scale Peer-to-Peer Systems. Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, Vol. 2218, p.329
Ben Y., 2001. Tapestry: An Infrastructure for Fault-
tolerant Wide-area Location and Routing. U. C.
Berkeley Technical Report UCB/CSD-01-1141
Buyya R., 2002. A Toolkit for the Modeling and
Simulation of Distributed Resource Management and
Scheduling for Grid Computing. The Journal of
Concurrency and Computation: Practice and
Experience (CCPE), Wiley Press
Chapin, 1999. Resource management in Legion. Future
Generation Computer Systems, v 15, n 5, p 583-594
Clip2, Gnutella Protocol Specifications v0.4,
http://www.clip2.com
Condor Project, http://www.cs.wisc.edu/condor/
Czajkowski, K.2001. Grid information services for
distributed resource sharing. High Performance
Distributed Computing, 2001. Proceedings. 10th IEEE
International Symposium, p 181 – 194
Ian F., 2001. On Fully Decentralized Resource Discovery
in Grid Environments. Lecture Notes In Computer
Science, Vol. 2242, p 51 – 62
Kaashoek MF., 2003. A Simple Degree-Optimal
Distributed Hash Table. Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, Vol. 2735/2003, p 98 – 107
Min C., 2004. A Peer-to-Peer Replica Location Service
Based on a Distributed Hash Table. Proceedings of the
ACM/IEEE SC2004 Conference, p 56
Ratnasamy S., 2001. A scalable content-addressable
network. Computer Communication Review, v 31, n 4,
p 161-172
Stoica, I., 2001. Chord: A scalable peer-to-peer lookup
service for internet applications. Computer
Communication Review, v 31, n 4, p 149-160
LEVEL HASH TABLE RESOURCE DISCOVERY MECHANISM IN GRID ENVIRONMENT
87
