
3D REGISTRATION AND MODELLING FOR FACE
RECOGNITION
Li Bai, Yi Song
School of Computer Science and Information Technology
University of Nottingham, Jubilee Campus, Wollaton Road,
Nottingham NG8 1BB, UK
Keywords: Registration, modelling, surface reconstruction, recognition.
Abstract This paper presents a new approach to automatic 3D face recognition using a model-based approach. This
work uses real 3D dense point cloud data acquired with a stereo face scanner. Since the point clouds are in
varied orientations, by applying a non-iterative registration technique, we automatically transform each
point cloud to a canonical position and detect facial features used for defining the frontal part of face which
is to be modelled in next step. Unlike the iterative ICP algorithm, our non-iterative registration process is
scale invariant. An efficient B-spline surface-fitting technique is developed to represent 3D faces in a way
that allows efficient surface comparison. This is based on a novel knot vector standardisation algorithm to
allow one-to-one mapping from the object space to a parameter space. Consequently, correspondence
between objects is established based on shape descriptors, which can be used for recognition.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent theoretical and technical advance in 3D data
capture opens up the possibility of overcoming the
difficulties in 2D face recognition systems due to
pose and illumination variations. Whereas most of
previous works use 2.5D (range) face images, this
work uses real three-dimensional (3D) data acquired
using a stereo vision based scanner. However, 3D
data (dense point clouds in this case) cannot be used
directly for shape analysis. First, the objects are in
varied orientations and sizes. Second, the surface
captured varies significantly across subjects and
often includes neck or shoulders. Third, since a data
set has around 30,000 vertices, it is impractical using
these vertices directly for recognition purposes. Thus
we are looking for a compact way to represent face
models so that they can be compared.
In this paper, a new approach to efficient 3D face
representation from unstructured point clouds is
presented. The paper is organised as follows. Section
2 describes our algorithms for simultaneous scale
invariant pose estimation and facial features
detection. Section 3 presents an efficient B-spline
surface reconstruction method, from which shape
descriptors are obtained to represent all face models
in a parameter space. With the affine-invariant
property of shape descriptors, normalisation and
alignment can be easily done as discussed in section
4. Correspondences between objects are also
obtained via the one-to-one mapping from the object
space to a parameter space. The distance metric is
then developed for face recognition. Finally, section
5 concludes the paper with the future research
directions.
2 REGISTRATION
2.1 Previous Work
In the past, several efforts have been made for the
registration of 3D point clouds. One of the most
popular methods is the iterative closest point (ICP)
algorithm developed by Besl and McKay (1992).
The ICP searches a pair of nearest points in two data
sets, and estimates a rigid transformation which
aligns the two points. The rigid transformation is
then applied to all the points of one data set to try to
match those of the second, and the procedure is
iterated until some optimisation criteria is satisfied.
Several variations of the ICP method have been
proposed. Chen and Medioni (1992) evaluated the
201
Bai L. and Song Y. (2006).
3D REGISTRATION AND MODELLING FOR FACE RECOGNITION.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 201-208
DOI: 10.5220/0001371002010208
Copyright
c
SciTePress

registration function using point-to-plane distance.
In Zhang (1994), a robust statistic threshold was
introduced to determine the matching distance
dynamically. Iterative methods such as this are
obviously time consuming. When the assumption of
one data set being a subset of the other is not valid,
false matches can be created (
Fusiello et al, 2002).
Moreover, they rely on a good estimate of the initial
transformation. Another deficiency of the ICP
method is scale sensitive. There are other alternative
approaches. For example, some feature-based
registration methods were presented in (
Godin et al,
1994; Godin and Boulanger, 1995;
Godin et al, 2001).
More detailed reviews on registration can be found
in (
Campbell and Flynn, 2001; Flusser and Zitova, 2003).
In face recognition, we have to register face
scans of varied sizes due to either the distinct
characteristics of each individual, e.g. faces between
child and adult, or the scale change of a scanner.
Moreover, the face surface varies significantly
across subjects and often includes neck or shoulders.
Finally, no transformation can be reasonably
estimated to pre-align two face scans.
2.2 Our Approach
The aim of registration is to define a transformation,
which takes a face of an arbitrary view to a
canonical position. The transformation can be
written as:
tDRkD +⋅⋅=
′
( 1 )
where D and D’ are the observed data before and
after transformation, respectively. R is a 3×3 rotation
matrix. The translation t and normalisation k can be
done using shape descriptors obtained from surface
reconstruction in section 3. The task at this stage is
to automatically find the rotation matrix, such that
D* = RD is in the canonical position. The rotation
matrix represents the pose estimate of the original
data set. The canonical position is defined as (in
world coordinate system), see Figure 2(c):
• The line linking two inner eye corners (E
left
,
E
right
) is perpendicular to the yz plane after
registration;
• The facial symmetry plane I is perpendicular to
the xy plane passing through nose tip N
tip.
• Both nose top N
top
and nose bottom N
bottom
are
located in plane I, and the line linking them is
perpendicular to the xz plane.
N
top
is defined as the intersection of the line linking
E
left
and E
right
and plane I
.
The nose tip can be
located during clouds generation.
Two stages are involved to obtain the rotation
matrix R and facial features. The first stage is to
estimate the initial rotation matrix (head pose) based
on the symmetry property of a face. Briefly, B-
spline curves are fitted to the point cloud, and the
resulting B-spline curves are measured against the
canonical coordinate axes to determine their
deviations from each axis to estimate the rotation
about that axis. The rotation matrix is the composite
of rotations around all the axes:
xiyiziapp
RRRR
⋅
⋅
=
( 2 )
Data will be near frontal after being transformed by
R
app
. Figure 1(a) illustrates the initial pose
estimation procedure and the result.
The next stage is to detect facial features and
refine the initial pose estimate, as shown in Figure
1(b). The nose saddle point is estimated first.
Possible areas containing inner corners of the eyes
can then be decided upon, as shown in Figure 1(c).
For each area, eight candidates of the inner eye
corners are obtained for further consideration. The
pair of points with the highest priority value is
chosen as the inner eye corners. Feature detection
and pose refinement are done in parallel, since the
coordinates of these features are directly related to
pose.
Pose refinement uses the following rotation
matrix:
zyxre
RRRR
⋅
⋅
=
( 3 )
where R
x
, R
y
and R
z
are the compensation rotation
matrices around x, y and z axes. The key idea of
pose refinement is to evaluate R
x
, R
y
and R
z
using
the facial feature points. As D* will be in the
canonical position after transforming the original
data with R=
appre
RR
•
, feature points must satisfy
the equations (4)-(10) simultaneously:
{}
⎪
⎪
⎭
⎪
⎪
⎬
⎫
⎪
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎪
⎨
⎧
−
′
+
=
∃
xtipxtop
n
xrightzyxleftzy
xtop
xtop
NN
ERRERR
N
N
,,
,
'
,
,
,
2
min
2
)(
.
Ι
( 4 )
where
′
left
E
and
′
right
E
are the candidate pair of inner
eye corners; n is number of candidate inner eye
corners
∑
=
′
=
=
=
m
i
yipi
yrightzyyleftzyytop
CsB
ERRERRN
0
,,
,,,
)(
( 5 )
∑
=
′
=
m
i
zipiztop
CsBN
0
,,,
)(
( 6 )
xtipxbottom
NN
,,
=
( 7 )
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
202

∑
=
′′
=
m
i
yipiybottom
CsBN
0
,,,
)(
( 8 )
∑
=
′′
=
m
i
zipizbottom
CsBN
0
,,,
)(
( 9 )
zbottomzztopz
NRNR
,,
=
(10 )
where
∑
=
m
i
ipi
CsB
0
,
)(
represents the face profile inferred
from the facial symmetry plane.
(a) (b)
© (d) (e)
Figure 1: Procedures of pose estimation and facial features
detection. (a) Initial pose estimate. (b) Refined pose
estimate. (c) Output from the first stage of pose estimation.
Possible areas containing the inner corner of eyes are
decided upon. (d) Candidates of the inner eye corners
chosen from the areas marked in (c). (e) Detected facial
features and the final output from the pose estimation
algorithm.
Figure 2 shows an example result of registering
original point clouds to a canonical position.
(a) (b)
(c)
Figure 2 Examples of original point clouds before and
after applying our registration algorithm. (a) Input point
clouds acquired from 3D scanner with varied orientations.
(b) Input point clouds displayed in texture. (c) Output
point clouds in the canonical position (in a same
orientation).
We will now compare our 3D registration
methods with the ICP algorithm. The ICP
registration results are shown in Figure 3 (b) and (e).
Figure 3 (c) and (f) are the results using our
approach.
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e) (f)
Figure 3: Comparison between ICP method and our
proposed method. (a) First pair of point clouds to be
registered. (b) Positive result from ICP method. (c) The
registration result using our approach. (d) Second pair of
input point clouds. (e) Negative result from ICP algorithm.
(f) Our result.
3 3D MODELLING
The 3D modelling problem can be stated as follows:
given a unstructured point cloud P: pi (xi, yi, zi),
find a B-spline surface F: R2 → R3, which fits the
point cloud best.
There has been considerable work on fitting B-
spline surfaces to 3D points. However, most work
dealt with fitting a single B-spline patch on a regular
grid data set. This can only deal with simple data
sets, e.g. a deformed quadrilateral (
Hoschek et al,
1989; Rogers and Fog, 1989; Sarkar and Menq, 1991)
or a deformed cylinder (
Schmitt et al, 1986). To
reconstruct complex surfaces, many efforts focus on
interconnecting multiple surface patches (
Eck et al,
1995; Eck and Hoppe, 1996; Krishnamurthy and Levoy,
1996; Milroy et al, 1995
). The problem with this is the
difficulty in having all objects modelled in the same
parameter space, since every patch has its own
parameter space.
3D REGISTRATION AND MODELLING FOR FACE RECOGNITION
203
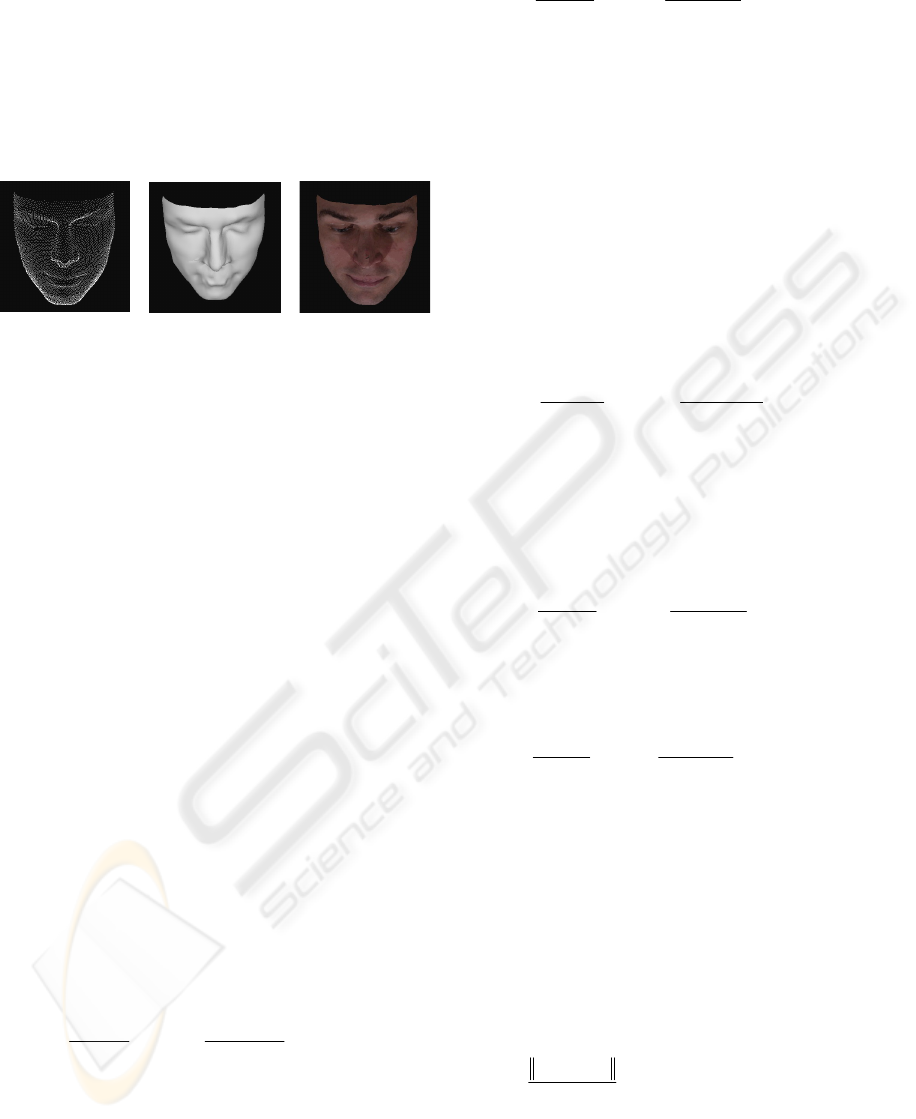

Our aim is to construct a compact and unique
representation of the 3D surface to allow face
comparison. This is achieved by constructing,
automatically, a single B-spline surface having C
k-1
continuity (k is the degree of B-spline function)
everywhere intrinsically, Figure 4(b), rather than
many patches stitched together. This makes object
comparison impossible.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 4: 3D modelling. (a) Unstructured point cloud to be
reconstructed. (b) Reconstructed surface. (c)
Reconstructed surface with texture mapping.
The procedure of constructing this single B-spline
surface is as follows:
• Decomposing the surface-fitting problem to a
sequence of curve-fitting problems based on a
knot vector standardisation algorithm. We
reconstruct a single B-spline surface on a
parameter space by the control points of the
surface and individual knot vectors. This is
discussed in section 3.2.
• Since the B-spline surface obtained from section
3.2 depends on the control points, parameter
values and basis functions, which vary from
individual to individual, there is no direct
mapping from the parameter domain to the
object space. The task in section 3.3 is to obtain
a direct one-to-one mapping relationship from
the object space to the parameter domain.
3.1 Knot Vector Standardisation
Given n
x
+1 control points f: {f
1
, f
2
, …, f
nx
} and a knot
vector X={x
0
, x
1
, …, x
nx+g+1
}, the B-spline curve F
of degree g is:
∑
=
=
X
n
i
igi
fxBxF
0
,
)()(
( 11 )
)()()(
1,1
11
1
1,,
xB
xx
xx
xB
xx
xx
xB
gi
igi
gi
gi
igi
i
gi −+
+++
++
−
+
−
−
+
−
−
=
Another B-spline curve L defined by n
Y
+1 control
points l: {l
1
, l
2
, …, l
ny
} and a distinct knot vectors
Y={y
0
, y
1
, …, y
ny+g+1
} is:
∑
=
=
Y
n
j
jgj
lyNyL
0
,
)()(
( 12 )
)()()(
1,1
11
1
1,,
yN
yy
yy
yN
yy
yy
yN
gj
jgj
gj
gj
jgj
j
gj −+
+++
++
−
+
−
−
+
−
−
=
The task is to standardise distinct knot vectorsand
have B-spline curves F and L defined on the same
knot vector.
Instead of simply merging all knot vectors
together (
Watt and Watt, 1992), our approach is to
standardise all knot vectors to a pre-defined knot
vector U={u
0
, u
1
, …, u
nu+g+1
}. Correspondingly,
control points set {f
i
} is re-calculated as
ff
U
X
n
k
n
i
′
== 00
α
( 13 )
Then curve F is:
∑
′
=
′
=
′
U
n
k
k
gk
f
xBxF
0
,
)()(
( 14 )
)()()(
1,1
11
1
1,,
xB
uu
xu
xB
uu
ux
xB
gk
kgk
gk
gk
kgk
k
gk −+
+++
++
−
+
′
−
−
+
′
−
−
=
′
( 15 )
Similarly, we have curve L defined on the same knot
vector U by
ll
U
Y
n
k
n
j
′
== 00
α
( 16 )
∑
′
=
′
=
′
U
n
k
k
gk
l
yNyL
0
,
)()(
( 17 )
)()()(
1,1
11
1
1,,
yN
uu
yu
yN
uu
uy
yN
gk
kgk
gk
gk
kgk
k
gk −+
+++
++
−
+
′
−
−
+
′
−
−
=
′
( 18 )
Comparing Equation (17) and (20), it is obvious that
the basis functions B’ and N’ are identical. We then
have one basis function expression Q for all B-spline
curves defined upon the knot vector U:
)()()(
1,1
11
1
1,,
sQ
uu
su
sQ
uu
us
sQ
gk
kgk
gk
gk
kgk
k
gk −+
+++
++
−
+
−
−
+
−
−
=
( 19 )
Consequently, Equation (11) and (12) can be
rewritten as:
∑
′
=
=
′
U
n
k
k
gk
f
sQsF
0
,
)()(
( 20 )
∑′
=
=
′
U
n
k
k
gk
l
sQsL
0
,
)()(
( 21 )
Errors E is measured between the set of original
data points D and the corresponding interpolated
values from B-spline curve F’. s
d
is the parameter
value associated with data point d. Then, we can
define E to be
Υ
Dd
d
d
sFd
E
∈
′
−
=
)(
( 22 )
The maximum error was within 1%. Therefore
we could ignore the difference between curve F’ and
F, by having F’ ≈ F.
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
204

3.2 B-spline Surface Fitting
A B-Spline surface
∑∑
==
=Γ
n
j
jihi
m
i
gj
CtNsBts
0
,,
0
,
)()(),(
( 23 )
is defined by
• a set of m+1 rows and n+1 column control
points
ji
C
,
, where 0 ≤ i ≤ m, and 0 ≤ j ≤ n;
• a knot vector of l+1 knots in the u- direction,
U={u
0
, u
1
, …, u
l
};
• a knot vector of k+1 knots in the v- direction,
V={v
0
, v
1
, …, v
k
};
• degree h in the u- direction; and
• degree g in the v- direction.
B
j,g
(s) is the B-Spline basis functions in the u-
directions, defined over knot vector U:
⎩
⎨
⎧
=
0
1
)(
0,
sB
j
( 24 )
)()()(
1,1
11
1
1,,
sB
uu
su
sB
uu
us
sB
gj
jgj
gj
gj
jgj
j
gj −+
+++
++
−
+
−
−
+
−
−
=
( 25 )
N
i,h
(t) is defined analogously over the knot vector V
in the v-direction.
Given grid data P: {p
c,d
| p
c,d
∈ R
3
, 0 < c < m, 0 <
d < n }, uniform knot vector U and V are obtained
for the u- and v- direction, respectively, basing on
the property of grid data spacing at equal intervals.
In this case, the fundamental identities, i.e. l=m+h+1
and k=n+g+1, can be held explicitly for the pair knot
vector U and V. Then the problem of finding the
underlying B-Spline surface Γ fitting P best can be
converted into a sequence of curve fitting processes
(Schmitt et al, 1986). However, for a complex surface,
e.g. face in
Figure 4 (a), obtaining grid data on all
areas such as forehead, nose and chin etc. is a
nontrivial problem. Alternative approaches are to
divide the surface into small planar patches and then
re-sample each patch to get grid data (
Krishnamurthy
and Levoy, 1996; Milroy et al, 1995; Eck and Hoppe,
1996
), which require extensive computation
subdividing the surface and maintaining continuity.
By applying the knot vector standardisation
algorithm described in 3.1, fundamental identity can
also be enforced on non-grid data. Thus non-grid
data can be decomposed into small portions upon
which the curve-fitting procedure can be applied
independently, as does on grid data. Consequently,
we can apply different automatic sampling schemes
on different parts of a face. For example, the
forehead area is rather flat with little curvature
changes. A sparse and evenly sampling scheme will
work well. In contrast, the area close to the nose
contains sharp curvature variations. A dense and
uneven sampling scheme is necessary to guarantee
precise interpolation.
Following the discussion above, the point cloud
data
}{:
3
RpP ∈
are decomposed into small portions
},,{:
10 m
pppP Λ
(sub dataset), where,
},,{:
0,01,00,00 x
pppp
Λ
, …,
},,{:
,1,0, xmmmmm
pppp Λ
and x
0
≠ x
1
≠ … x
m
. For each sub dataset
c
p , 0 ≤ c
≤ m, the curve-fitting procedure is applied
independently:
∑
=
=
xc
d
cddgdcd
QsBp
0
,
)(
( 26 )
After standardising knot vectors, Equation 26 is
written as
∑
=
=
n
j
jcdgjcd
QsBp
0
,,
)(
( 27 )
where
∑
=
=
m
i
jichijc
CtNQ
0
,,,
)(
( 28 )
From Equation 27 and 28, the underlying B-Spline
surface is calculated as:
∑∑
==
=
n
j
m
i
jichidgjcd
CtNsBp
00
,,,
))()((
∑∑
==
Γ==
n
j
cdjichi
m
i
dgj
tsCtNsB
0
,,
0
,
),()()(
( 29 )
3.3 Shape Descriptors
After B-spline surface-fitting, we have each face
modelled by a set of control points over its own pair
of knot vectors. If we use matrix operations to
present the reconstructed B-spline surface, i.e.
Equation (23), we have:
)())(),((),(
C
N
B
kk
k
k
vectsts •Α=Γ
( 30 )
where matrix A represents the Kronecker product.
Obviously Equation (30) is not a direct function of
parameter (s, t) yet. By applying knot vector
standardisation, we can remove the dependency on
individual knot vectors in Equation (30). By having
),())(),(( tsts
A
N
B
k
k −
Αα
( 31)
CC
kk
vec
′
α)(
( 32 )
if u
j
≤ s <u
j+1
otherwise
3D REGISTRATION AND MODELLING FOR FACE RECOGNITION
205
where
A
−
is a function of (s,t) for all face models.
C
k
′
is a set of parameters ∈ R
3
which is independent
of individual knot vectors, we arrived at
C
A
k
k
tsts
′
⋅=Γ
−
),(),(
( 33 )
Thus we have established a direct mapping between
the parameter domain (s, t) ∈ Ω: [0,1]×[0,1] and the
object space Γ ∈ R
3
. From Equation (33), we know
that
C
′
defines the unique shape of a surface,
i.e.
C
′
is a shape descriptor. Figure 4(b) shows a
rendered B-spline surface using shape descriptors
over the domain Ω. Shape descriptors have several
important properties, including:
• Establishing direct one-to-one mapping
relationship from the parameter domain to the
object space. For each pair of parameter value
(s, t), we have a unique corresponding B-spline
surface point in the object space.
•
Compact representation for 3D objects. The
approach can achieve over 90% compression
rate with similar rendering result to polygon
representation.
•
Affine-invariance. The same result will be
obtained transforming a B-spline surface itself
or its shape descriptors. This is a very important
property and will be used in next section for
normalisation and alignment. Instead of
translating and scaling the 3D object directly,
we will apply the operations to its shape
descriptors.
4 FACE RECOGNITION
We have represented 3D face scans in a form which
can be used to compare faces. In this section, we
will use this representation to match test faces to
those stored in a database. Currently, our database
consists of 30 individuals, 3 scans per individual.
One scan is used to construct the 3D face database,
whilst the other 2 scans are used in face recognition
experiments. The test set consisted of 24 individuals
with 2 scans for each.
Each face in the database and test set is modelled
using the techniques discussed in previous sections.
Each object in the test set is compared against all the
faces in the database. The face having the smallest
difference is identified as the best match to the test
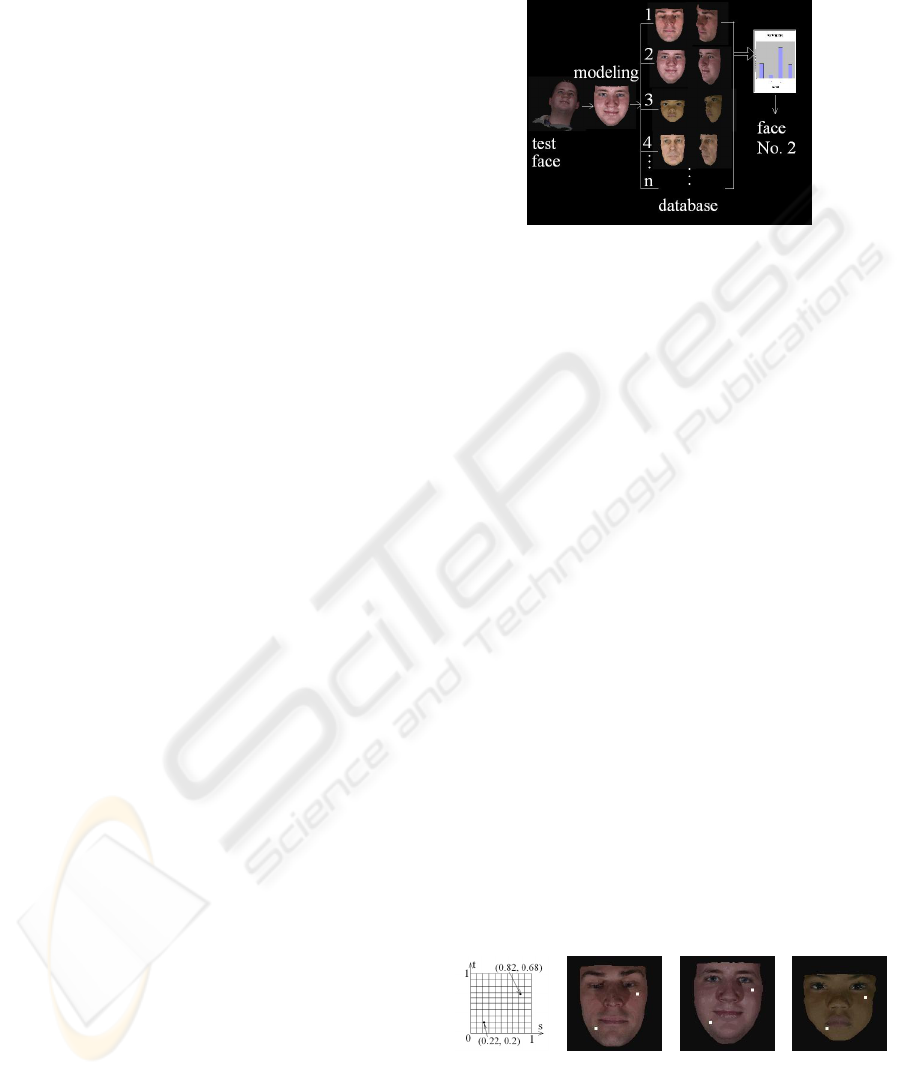
face. The procedure is shown in Figure 5. Details of
the implementation is described below.
Figure 5: Face recognition based on the distance metric.
4.1 Face Comparison
We normalise and align face models first. As
mentioned in section 3, normalisation and alignment
can be done fairly straightforwardly using the affine-
invariant property of shape descriptors. Taking one
model in the database as the generic model, we
normalise and align all the face models to the
generic model.
tk
CC
kk
+⋅=
′′′
( 34 )
where k and t are scalars of normalisation and
translation, respectively. The normalised and aligned
face model is:
C
A
k
k
tsts
′′
⋅=Γ
−
),(),(
( 35 )
The corresponding surface points between
models can be generated due to the one-to-one
mapping from the parameter domain Ω to the object
space. For each pair of parameters (s, t), each face
model has a unique corresponding B-spline surface
point:
),(),( tsts
k
Γ⇒
( 36 )
),(),(
1
tsts
k +
Γ⇒
( 37 )
Therefore, B-spline surface points Γ
k
(s, t) and Γ
k+1
(s,
t) are uniquely mapped, i.e.
),(),(
1
tsts
kk +
Γ⇒Γ
( 38 )
Examples are shown in Figure 6.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 6:Corresponding B-spline surface points. (a) A
common parameter domain
Ω. (b)-(d) Face models
reconstructed on the parameter domain,
Ω in (a). For each
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
206
parameter pair marked in (a), there is a unique surface
point on each face model.
By sampling the parameter domain, we obtain a set
of corresponding B-spline surface points on each
face model. The linear distance-based method, i.e.
Euclidean distance matrix analysis (EDMA) (
Lele
ans Richtsmeier, 2001
) can be used as metric to judge
the similarity between a test face and each face in a
database, which is given by
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎭
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎬
⎫
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎨
⎧
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
Γ−Γ−
Γ−Γ
∑∑
∑∑
∑∑
==
=
≠
=
≠
=
≠
=
≠
=
n
t
m
s
n
t
tt
m
s
ss
testtest
n
t
tt
m
s
ss
ii
N
i
tsts
tsts
00
0'
'
0'
'
0'
'
0'
'
0
)','(),(
)','(),(
min
( 39 )
where Γ
i
represents the i
th
model in the database;
Γ
test
is a test object which we want to find its
matching face model in the database. N is the total
numbers of the 3D models in the database. Small
values indicate a high degree of similarity.
4.2 Experimental Results
The representative 3D models and test scans are
shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8 respectively.
Figure 7: Some of the 3D face models in the database.
Figure 8: Representative test faces.
Each face in the data set is compared against all the
3D models in the database. The examples of
similarity measurement between test faces and each
face in a database are provided in Figure 9.
Figure 9: Similarity measurement. The bar charts show the
similarity between a test face and each face in a database.
The face having the smallest difference to the test face is
identified as the best match to the test face.
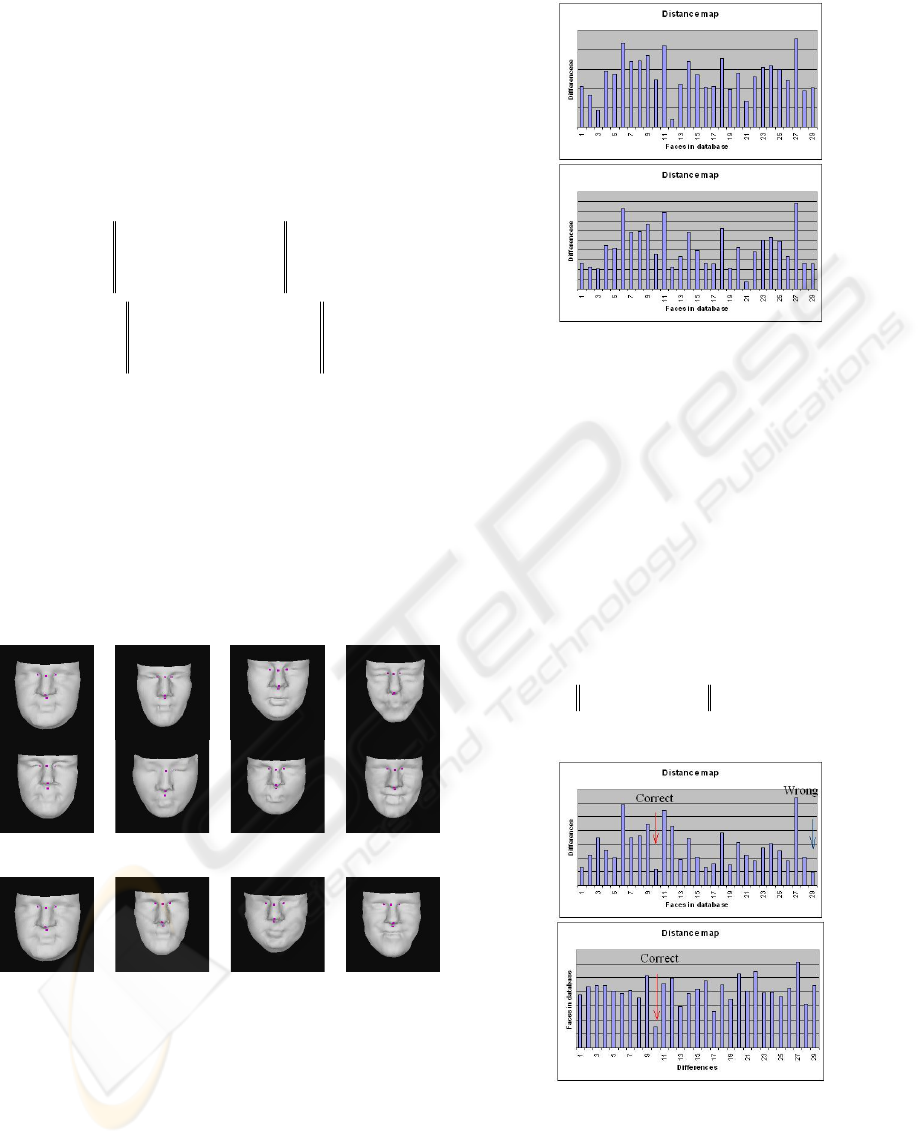
Out of the 4 errors in the 48 test faces
(corresponding to 91.7% accuracy), 2 test faces are
different scans of the same subject with different
facial expressions. In the other two cases, the correct
match is ranked the second best, Figure 10(top).
However, incorporating some additional
information, e.g. using the square root distance
between corresponding points as an additional
metric to compare the similarity, given by Equation
40, they are correctly identified, Figure 10(bottom).
⎭
⎬
⎫
⎩
⎨
⎧
Γ−Γ
∑∑
==
=
n
t
m
s
testi
N
i
tsts
00
2
0
),(),(
min
( 40 )
Figure 10: The difference between the test face and the
impostor face. (Top) The correct model is the second
ranked face in the database. (Bottom) Result after
combining another recognition strategy.
3D REGISTRATION AND MODELLING FOR FACE RECOGNITION
207

5 CONCLUSION
We have developed a new automatic model-based
face recognition system, which includes both non-
iterative registration and the representation of 3D
face models by shape descriptors. By registering
point clouds to a canonical position, we overcome
the pose-variation problem. Unlike ICP algorithm,
this non-iterative registration process is scale
invariant. An efficient B-spline surface-fitting
technique is developed to reconstruct underlying
surface for the registered data set. A new knot vector
standardisation technique is proposed to allow a
direct one-to-one mapping relationship from the
object space to a parameter space. Subsequently, a
compact parametric representation of 3D objects is
obtained. The system has been tested on a personal
computer (Pentium 4/512M RAM). Compared with
the existing method of closed surface
parameterisation, which takes 33s to 536s depending
on the complexity of the objects [BGK96], the
registration and modelling process introduced in this
paper only takes 2 seconds, on an average sized
point cloud (about 25,000 vertices).
Although surface distance can be used as a
metric for face recognition, it may not be very
sufficient since no explicit geometric information is
employed. Our future work is to integrate geometric
information into recognition methods. For example,
we may turn a recognition problem into a
classification problem of the shape descriptors.
With the proposed surface representation, it is
possible to analyse facial component separately. As
the geometry of B-spline surface can be inferred
from the shape descriptors, we can delineate facial
areas, e.g. forehead, nose, mouth, chin, from the
parameter space, and weigh each part separately in
the recognition metric to reduce the influence of
facial expression. The areas potentially affected by
facial expression will be given lower weight.
REFERENCES
Besl, P.J., and McKay, N.D. (1992) A Method for
Registration of 3D Shapes. IEEE Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, vol. 14, No. 2, 239-256.
Chen, Y., and Medioni, G. (1992) Object modelling by
registration of multiple range images. Image and
Vision Computing, vol. 10, No. 3, 145-155.
Campbell, R., Flynn, P. (2001) A Survey of Free-form
Object Representation and Recognition Techniques,
Computer Vision and Image Understanding, vol. 81,
pp. 166-210.
Eck, M., DeRose, T., Duchamp, T., Hoppe, H.,
Lounsbery, M., and Stuetzle, W. (1995)
Multiresolution Analysis of Arbitrary Meshes. In
Computer Graphics (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH’ 95),
pages 173-182.
Eck, M., and Hoppe, H. (1996) Automatic Reconstruction
of B-Spine Surfaces of Arbitrary Topological Type.
Proc. 23rd Int'l. Conf. on Computer Graphics and
Interactive Techniques SIGGRAPH '96, ACM, New
York, NY. pp. 325-334.
Fusiello, A., Castellani, U., Ronchetti, L., and Murino, V.
(2002) Model Acquisition by Registration of Multiple
Acoustic Range Views, Computer Vision, ECCV2002,
Springer, pp. 805-819.
Flusser, J. and Zitova, B. (2003) Image Registration
Methods: A Survey, Image and Vision Computing,
vol. 21, pp. 977-1000.
Godin, G. and Boulanger, P. (1995) Range Image
Registration Through Viewpoint Invariant
Computation of Curvature, IAPRS, 30 (5/W1), pp.
170-175.
Godin, G., Rioux, M. and Baribeau, R. (1994) Three-
dimensional Registration Using Range and Intensity
Information, SPIE, vol. 2350, Videometrics III, pp.
279-290.
Godin, G., Laurendeau, D. and Bergevin, R. (2001) A
Method for the Registration of Attributed Range
images, International Conference on 3D Imaging and
Modeling, Quebec, pp. 179-186.
Hoschek, J., Schneider, F. –J. and Wassum, P. (1989)
Optimal Approximate Conversion of Spline Surfaces,
Computer Aided Geometric Design, vol. 6, issue 4, pp.
293-306.
Krishnamurthy, V. and Levoy, M. (1996) Fitting Smooth
Surfaces to Dense Polygon Meshes, ACM-0-89791-
746-4/96/008.
Lele, S. and Richtsmeier, J. (2001) An Invariant Approach
to the Statistical Analysis of Shapes. Boca Raton:
Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Milroy, M., Bradley, C., Vickers, G. and Weir, D. (1995)
G1 Continuity of B-spline Surface Patches in Reverse
Engineering. CAD 27, 471-478.
Rogers, D. and Fog, N. (1989) Constrained B-spline Curve
and Surface Fitting, Computer Aided Design, vol. 21,
pp. 641-648.
Schmitt, F., Barsky, B. and Du, W. H. (1986) An Adaptive
Subdivision Method for Surface Fitting from Sampled
Data. Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH’ 86
Proceedings), volume 20. pp. 179-188.
Sarkar, B. and Menq, C. (1991) Parameter Optimization in
Approximating Curves and Surfaces to Measurement
Data, Computer Aided Geometric Design, vol. 8, pp.
267-290.
Watt, A. and Watt, M. (1992) Advanced Animation and
Rendering Techniques: Theory and Practise. Addison-
Wesley.
Zhang, Z. (1994) Iterative Point Matching for Registration
of Free-form Curves and Surfaces. International
Journal of Computer Vision, vol. 13, No. 2, pp.119-
152.
VISAPP 2006 - IMAGE UNDERSTANDING
208
