
MEDIATION WITHOUT A GLOBAL SCHEMA
Matching Queries and Local Schemas Through an Ontology
Michel Schneider, Damien Thevenet
LIMOS, Complexe des Cézeaux, 63170 AUBIERE Cedex
Keywords: Interoperability, Heterogeneity, Mediation, Matching.
Abstract: Approaches by mediation to make multiple sources interoperable were essentially investigated when one are
able to resolve a priori the heterogeneity problems. This requires that a global schema must be elaborated or
that mappings between local schemas must be established before any request can be posed. The object of
this paper is to study to what extend a mediation approach can be envisaged when none of these features are
a priori available. Our solution consists in matching a query with each of the local schema by using an
ontology of the domain. Such a solution is particularly suitable when sources are liable to evolve all the time.
We are investigating this solution by considering the mediation of heterogeneous XML sources. Local
schemas are represented in the OWL language. Queries are formulated using an XQUERY-like language.
Matching of names is solved by using the an ontology of the domain. We have developed a prototype and
conducted a number of experiments to evaluate the capacity of the approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
The interoperability of multiple heterogeneous
sources represents an important challenge
considering the proliferation of numerous
information sources both in private networks
(intranet) and in public networks (internet).
Heterogeneity is the consequence of the autonomy:
sources are designed, implemented and used
independently. Heterogeneity can appear for
different reasons: different types of data, different
representations of data, different management
software packages. The interoperability consists in
allowing the simultaneous manipulation of these
sources so as to link the data which they contain. It
is necessary to make different sources interoperable
in numerous domains such as electronic business,
the environment, the economy, medicine, genomics.
Interoperability problems occur in very different
ways depending on whether sources are structured
(data bases), semi-structured (HTML or XML
pages), non-structured (any file). The access
interfaces also influences the possibilities of
interoperability. For example two data bases can be
difficult to make interoperable when they are only
accessible through specific web interfaces.
One interoperability approach which has been
studied for several years is based on mediation
(Wiederhold, 1992), (Garcia-Molina, 1997). A
mediator analyzes the query of a user, breaks it
down into sub-queries for the various sources and
re-assembles the results of sub-queries to present
them in a homogeneous way. The majority of
mediation systems operate in a closed world where
one knows a priori the sources to make interoperable.
There are several advantages to this. First it is
possible to build an integrated schema which
constitutes a reference frame for the users to
formulate their queries. Then it is possible to supply
the mediator with various information which are
necessary for the interoperability and particularly to
resolve heterogeneity problems. The different kinds
of heterogeneity to be resolved are now clearly
identified: heterogeneity of concepts or intentional
semantic heterogeneity; heterogeneity of data
structures or structural semantic heterogeneity;
heterogeneity of values or extensional semantic
heterogeneity. Different solutions has been studied
and experimented on to solve these problems. For
example we can cite the work of (Hull, 1997) and
(Kedad, 1999). From these initial investigations,
very numerous works intervened to propose
automatic approaches of integration of schemas. An
approach was particularly investigated: the mapping
of schemas. It led to the elaboration of several
systems such as SEMINT, LSD, SKAT, DIKE,
COMA, GLUE, CUPID. One will find analyses and
comparisons of such systems in (Rahm, 2001) or
5
Schneider M. and Thevenet D. (2006).
MEDIATION WITHOUT A GLOBAL SCHEMA - Matching Queries and Local Schemas Through an Ontology.
In Proceedings of WEBIST 2006 - Second International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - Internet Technology / Web
Interface and Applications, pages 5-12
DOI: 10.5220/0001249700050012
Copyright
c
SciTePress
(Hai Do, 2002) or (Mohsenzadeh, 2005). The
practical aspects of the application of such systems
are discussed in (Berstein, 2004). The role of
ontologies was also investigated. In (Cui, 2001) and
(Missikoff, 2004), the interest of ontologies for the
semantic interoperability is underlined. Several
approaches of integration of information based on
ontologies were suggested. One will find a synthesis
of it in (Wache, 2001). It is necessary also to quote
the work of (Lenzerini, 2005) suggesting a logical
frame for the integration of data. In every case, the
objective is to build a global schema which
integrates all the local schemas.
When one operates in an evolutionary world
where sources can evolve all the time, the
elaboration of a global schema is a difficult task. It
would be necessary to be able to reconstruct the
integrated schema each time a new source is
considered or each time an actual source makes a
number of changes. In this paper we suggest an
approach which does not require a preliminary
integration of sources schemas but which is based on
a matching between the user query and each source
schema. The user query is formulated with regard to
a domain specified through an ontology. Only the
sources whose schemas match with the query are
considered. The user query is rewritten for each of
these sources according to its information capacity.
These sources are then interrogated. Results are
formatted and integrated.
This approach offers several advantages.
Integration is processed only on the schemas of the
results and not on the entire schemas of all potential
sources. The rewriting process is simpler.
The paper is organised as follows. In section 2
we give an overall presentation of our approach.
Section 3 is devoted to the query language and
section 4 to the OWL representation of sources. In
section 5 we explain the main features of our
matching algorithm. Section 6 is relative to the
rewriting of a query. Section 7 is devoted to some
experiments with a prototype of the system. Section
8 presents a number of conclusions and perspectives.
2 PRESENTATION OF THE
APPROACH
The approach which we propose does not use a
global schema. The user thus formulates his query
by using his implicit knowledge of the domain or by
making an explicit reference to an ontology of the
domain.
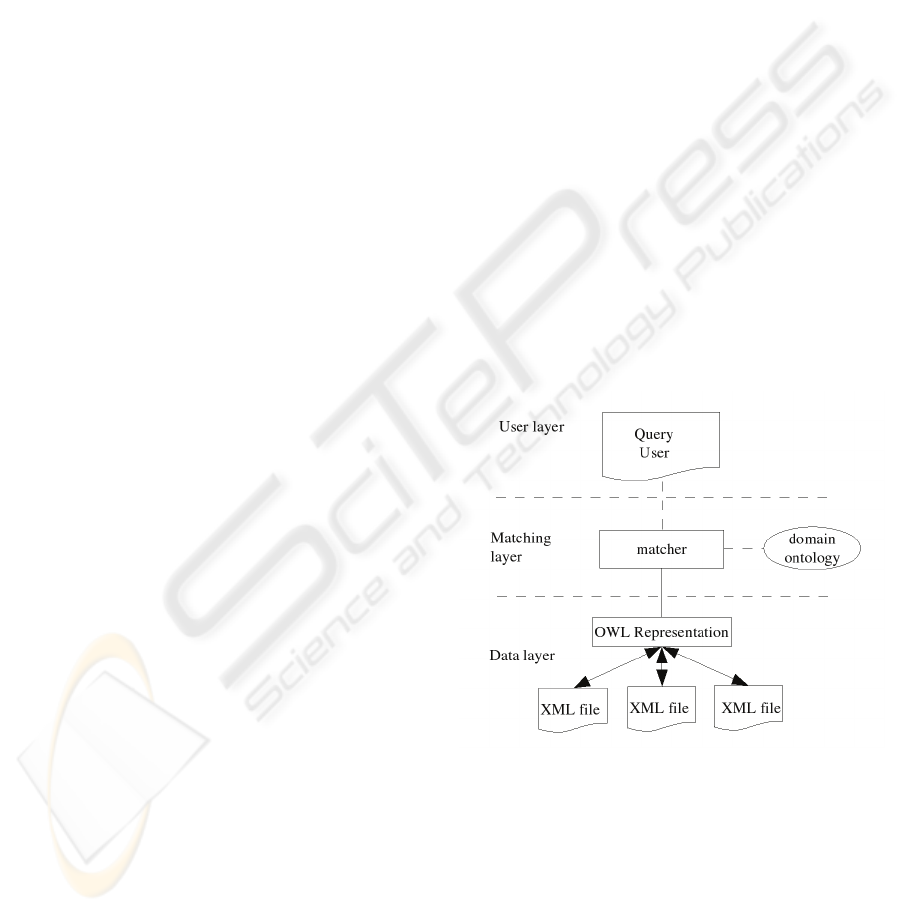
The matcher is the central element of the system.
It receives the user query, and has the task to
determine if this query can be applied to a data
source (figure 1). To achieve this processing, it
possesses a representation of each data source in a
common formalism (we propose OWL to support
this formalism, cf section 3). It must search for a
correspondence between the query and each source
by taking into account the terms and the structure of
the query. Intuitively, so that a source can answer a
query, the terms of the query must correspond to
those of the source and the structure of the query
must correspond to that of the source.
We propose a query language based on a
simplified version of XQUERY. The structure of a
query is thus defined through the various paths
which appear in the clauses FOR, LET, WHERE. A
correspondence is established with a source if each
of these paths has a correspondent in the OWL
representation of the source. More exactly, let E
1
, E
2
,
…, E
k
be a path. There is correspondence if one can
find in the OWL representation classes C
1
, C
2
, …,
C
k
such that C
j
is a synonym or hyponym of E
j
for
j∈[1, k] and such that every couple of classes C
i
,
C
i+1
for i∈[1, k-1] is connected by a composition of
properties in the OWL representation. In other
words, it is necessary to find a subset of the OWL
representation which is subsumed by the path. The
notions of synonym and hyponym are defined
through the ontology of the domain.
For example consider the following query
specified with our simplified XQUERY language :
Q : for $a in supplier, $b in customer
where $b/name = "Ronald" and
$a/region = $b/region
return <b> {$b}</b>
It looks for customers with name “Ronald” and
living in the same region as a supplier.
Figure 1: The architecture of our syste
m
.
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
6
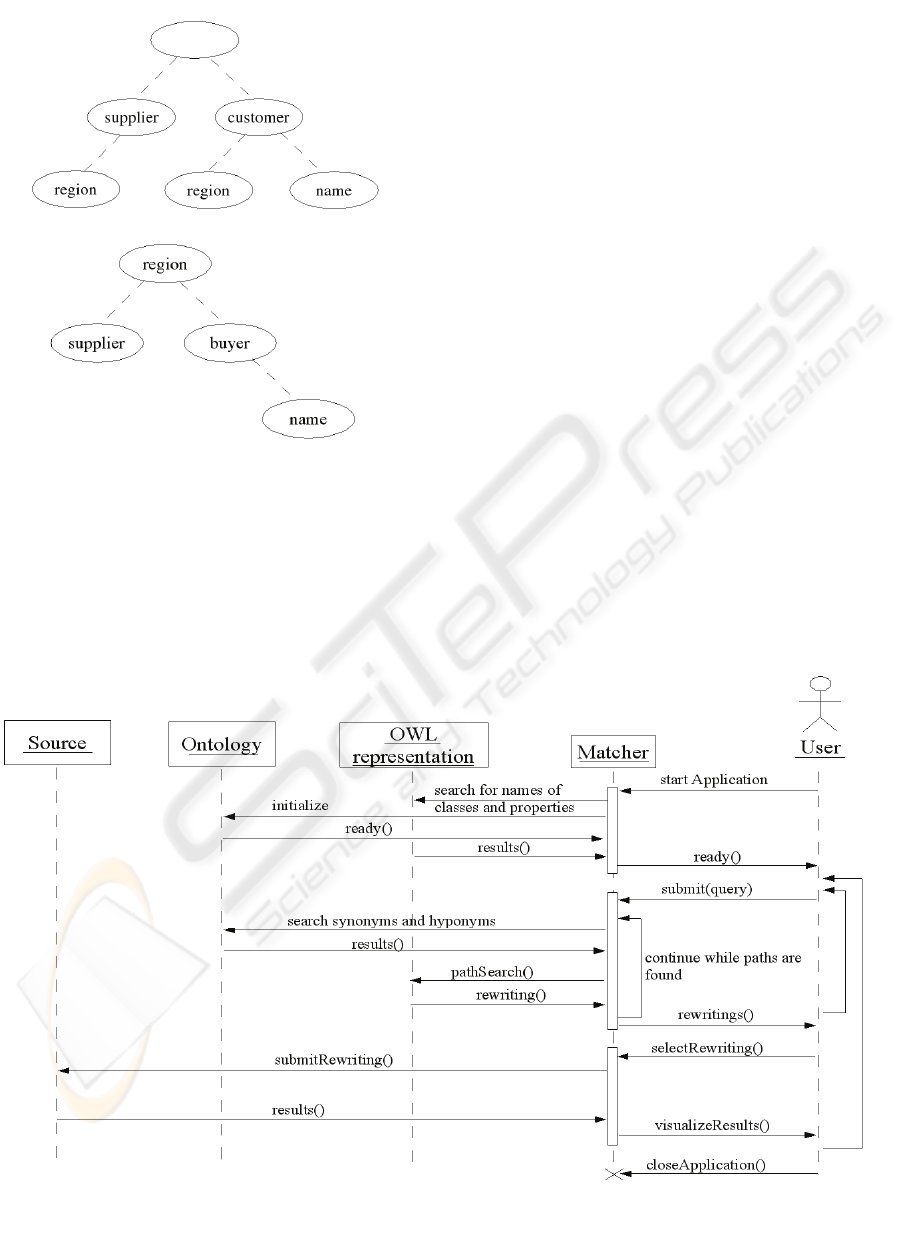
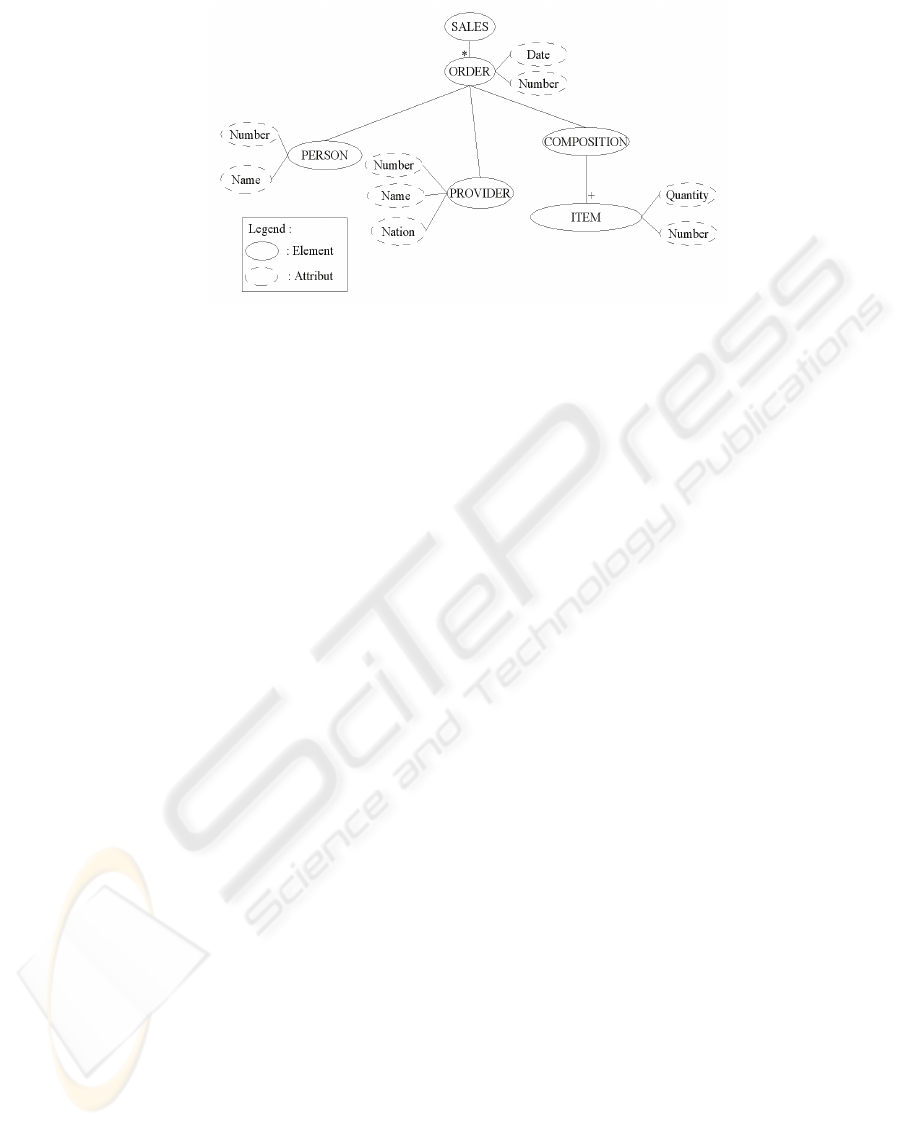
Consider the two semi-structured sources of
figure 2.
It is straightforward to infer that the query
matches with the first source since the supplier
element and the customer element both have a son
element the name of which is region. The matcher
must then check that this son element occurs only
once. A matching for second source cannot be
inferred so easily. First the matcher must discover
that buyer is an hyponym of customer. Then it must
scan the hierarchy upward in order to establish that a
supplier and a buyer are both connected to a unique
region. So this second source is also a candidate for
a rewriting of query Q.
We are now able to comment on the working of
our system which is shown by the UML diagram of
figure 3.
In the first phase the system initializes the
connection with the ontology and gets back the
names of the classes and the properties in the OWL
representation. The system is then ready to handle
queries.
In the second phase, when the system receives a
query, it first interrogates the ontology to retrieve the
synonyms and the hyponyms of the terms of the
request. It then initiates the operation of matching
for each of the paths of the query. Several rewriting
possibilities can be proposed. To avoid inconvenient
rewritings, we consider only the hyponyms of levels
1 to 3.
The third phase corresponds to the execution of
one of these rewritings on the source concerned. It
may be necessary to transform the rewriting. This
operation is performed with a wrapper associated to
the source.
Figure 3: The working of our system.
Fi
g
ure 2: Two semi-structured sources.
MEDIATION WITHOUT A GLOBAL SCHEMA - Matching Queries and Local Schemas Through an Ontology
7
3 QUERY LANGUAGE
Our query language is a simplified version of
XQuery. The user will have the possibility of using
the FLWR construct of XQUERY with limitations
indicated below.
- Since the user does not know the documents
which can provide an answer, names of documents
are omitted. So the root of a path is the name of an
element. The system will make searches in all the
documents having the root names in their description.
- Since the user does not know the structure of
the data sources, it is not possible for him to decide
if a term corresponds to an element or to an attribute.
However he has the possibility of using the symbol
'@' to indicate that he wants to search for an
attribute. The system will first look for a
correspondence with an attribute, but if this is not
possible, it will continue its search on elements. If
the symbol '@' is not present, the search will be
made at the same moment on elements and attributes.
- Also, it is impossible for the user to know
whether two elements are directly connected or if
there are one or several intermediate elements. So it
is not possible to differentiate the descent of one
level "/" and the descent of several levels " // ". So
the system will be responsible for testing the descent
at several levels.
- The functions of XPATH are not implemented
in the simplified version.
- No difference is made in the query user
between lower case and upper case letters. The
system will make sure the exact writing of a term is
retrieved for the rewriting of the request.
4 OWL REPRESENTATION OF
THE SOURCES
We chose to represent the sources schemas with
OWL for various reasons. First it is possible to
transform semi-structured schemas (XML
documents) and structured schemas (relational
databases, object databases) into OWL and OWL
thus appears to be a good candidate for a pivot
language. Then, with a view to our matching
operation, it is easy to determine the connections
between classes in an OWL file (as stated above,
the matcher must discover paths in the source which
are subsumed by a path in the query). Finally, with
OWL it is possible to take advantage of the formal
frame of the description logics.
We elaborated an algorithm with which a DTD
can be mapped into an OWL representation. This
mapping is bijective: from the OWL representation,
it is possible to regenerate the DTD.
The main idea is to represent every element of
the DTD by an OWL class. Every father-son link
between two elements is then represented by an
OWL property. An attribute is also represented by a
property. When a father element has only a single
son element, the cardinality of this son is represented
by creating a restriction on the property connecting
the two elements. When the father element is a
complex element, we add an intermediate class to be
able to express correctly all the cardinalities.
Agreements for the names of classes and
properties are as following. The class representing
an element will be named with the name of the
element. For an intermediate class (associated to a
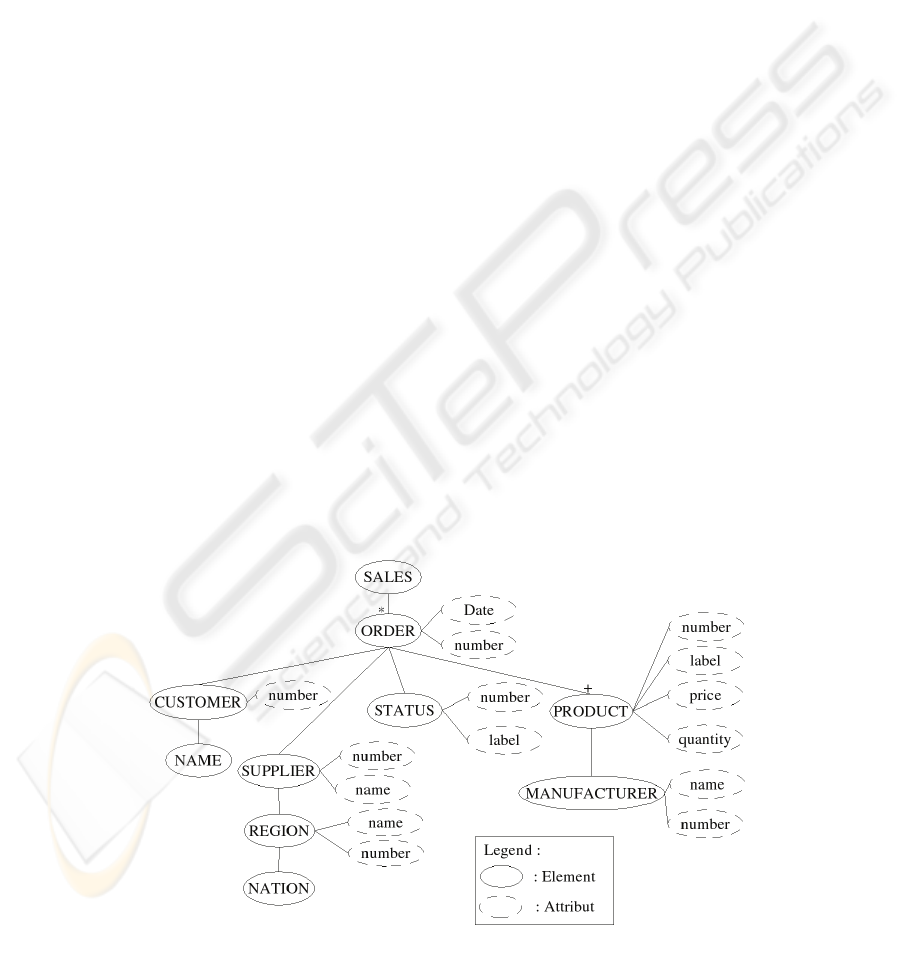
Fi
g
ure 4: The semi-structured source A.
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
8
complex element), the name of the class will contain
the names of elements with their separator, quite in
brackets. When this name is long, an entity can be
used. A property between two classes will carry the
two names separated by a point. For attributes, the
symbol '@' is used to separate the name of the class
and the name of the attribute.
As an example let us consider the element
ORDER of the source A, the schema of which is
shown in figure 4.
In the DTD, the definition of this element is:
<!ELEMENT ORDER(CUSTOMER, STATUS,
SUPPLIER, PRODUCT+)>
In order to obtain its OWL representation, a class
ORDER is created and also an intermediate class the
name of which is (CUSTOMER, STATUS,
SUPPLIER, PRODUCT+). For clearer
understanding, the entity &complexe1 is introduced
to replace this name in the OWL file. Then a
property connecting ORDER with the complex class
is created, and the cardinality in the class ORDER is
restricted. In the definition of the complex class the
limitations of cardinalities are introduced for each of
the elements. For CUSTOMER, STATUS and
SUPPLIER, the cardinality is forced to be 1. Then
properties are created to connect the complex class
with each of the classes CUSTOMER, STATUS,
SUPPLIER and PRODUCT (figure 5).
Using the same principles, it is possible to design
an algorithm which maps a relational schema into a
similar OWL representation. So our approach can be
extended to deal also with relational sources.
5 MATCHING ALGORITHM
We have to find a matching for each of the paths of
the query.
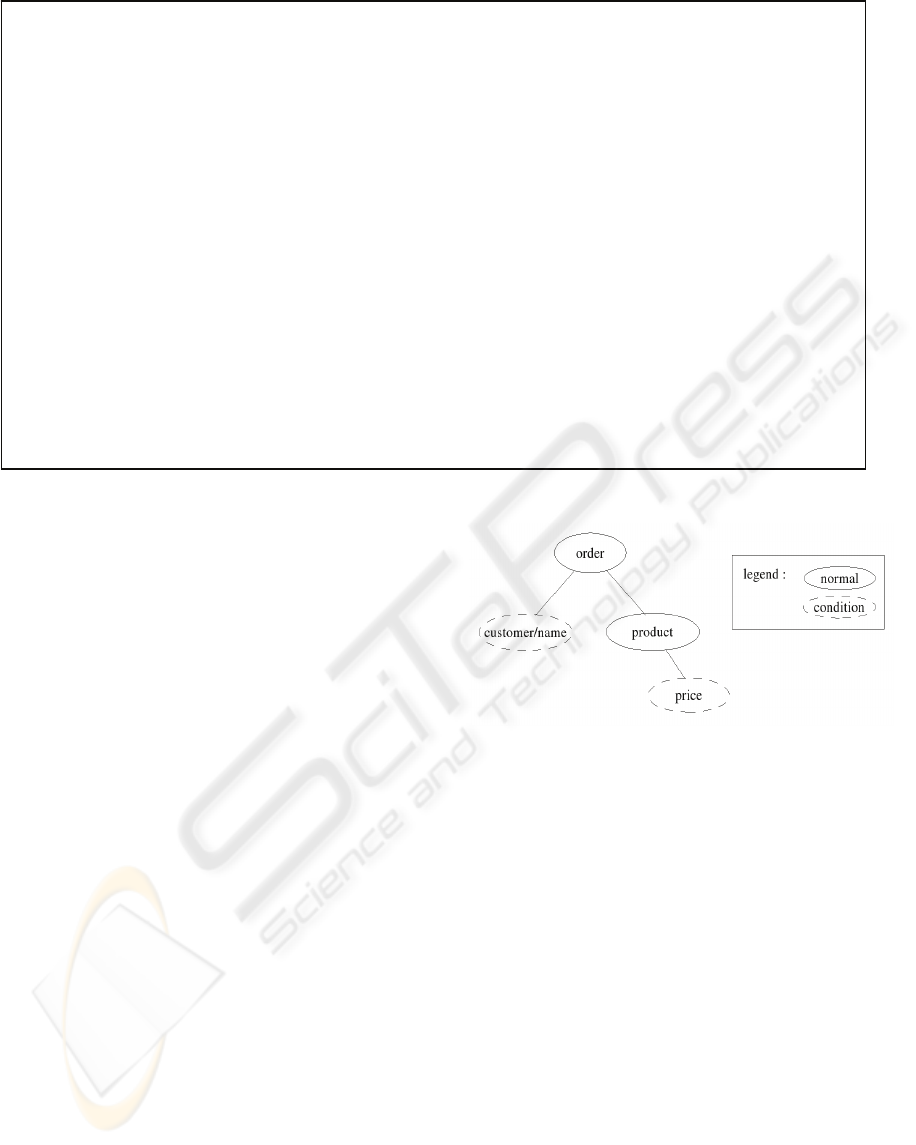
To make the matching we represent a path as a
tree having normal nodes and condition nodes. For
example the path
order[customer/name="Pierre"] /product[price>15]
is represented by the tree in figure 6. A simple path
composed only of a succession of terms separated by
the symbol / is associated to every node.
The matching of a path is then made through two
main functions matchSimplePath(SP) and
matchPath(P).
The function matchSimplePath(SP
i
) looks in the
OWL representation for the simple paths SP
ij
which
have a matching with SP
i
. For example, let
Figure 5: OWL representation for the ORDER element and its sons in source A.
<owl:Class rdf:ID="ORDER"> <rdfs:subClassOf> <owl:Restriction>
<owl:onProperty rdf:resource="#ORDER.&complex1;"/>
<owl:cardinality rdf:datatype="&xsd;nonNegativeInteger"> 1 </owl:cardinality>
</owl:Restriction> </rdfs :subClassOf> </owl:Class>
<rdf:Property rdf:ID="ORDER.&complex1;">
<rdfs:domain rdf:resource="#ORDER"/> <rdfs : range rdf:resource="#&complex1;"/>
</rdf:Property>
<owl:Class rdf:ID="&complex1;">
<rdfs:subClassOf> <owl:Restriction>
<owl:OnProperty rdf:resource="#&complex1;.CUSTOMER"/> <owl:cardinality
rdf:datatype="&xsd;nonNegativeInteger"> 1 </owl:cardinality> </owl:Restriction> </rdfs :subClassOf>
…….
<rdfs:subClassOf> <owl:Restriction>
<owl:OnProperty rdf:resource="#&complex1;.PRODUCT"/> <owl:minCardinality
rdf:datatype="&xsd;nonNegativeInteger"> 1 </owl:minCardinality> </owl:Restriction> </rdfs :subClassOf>
</owl:Class>
<rdf:Property rdf :ID="&complex1;.CUSTOMER">
<rdfs : domain rdf:resource="#&complex1;"/>
<rdfs:range rdf:resource="#CUSTOMER"/>
</rdf:Property>
Fi
g
ure 6: The tree corres
p
ondin
g
to a
p
ath.
MEDIATION WITHOUT A GLOBAL SCHEMA - Matching Queries and Local Schemas Through an Ontology
9

SP
i
=E
1
/E
2
/E
3
. A path SP
i1
matches with SP
i
if E
1
, E
2
,
E
3
have correspondents C
1
, C
2
, C
3
in the source and
if C
1
is connected to C
2
and C
2
is connected to C
3
. E
j
corresponds to C
j
if E
j
or an E
j
's synonym or an E
j
's
hyponym is identical to C
j
. C
1
is connected to C
2
if
C
1
and C
2
are connected either by a direct or inverse
property or either by a composition of direct or
inverse properties.
In the tree of the path P
i
, the set of paths SP
ij
which have a matching with P
i
is associated to every
node N
i
(SP
i
). A node will thus be represented by
N
i
(SP
i
, SP
ij
j∈[1, k]).
The function matchPath(P) tests whether if a
correct assembly of simple paths can be found which
corresponds to the tree of P. Let N
i
be a node of the
tree and N
i+1
one of its sons. One says that the
assembly between N
i
and N
i+1
is correct if the last
element of one of the simple paths SP
im
is connected
with the first element of one of the simple paths
SP
i+1,n
. The function matchPath(P) supplies all the
possible correct assemblies. Each of these
assemblies represents a path in the source which has
a matching with P.
6 REWRITINGS OF THE QUERY
To rewrite a query with regard to a source one looks
for a rewriting of each of its paths. The rewriting of
a path P
i
then consists in replacing it in the query by
one of the paths P
ik
which matches with P
i
and in
inserting the navigation operators between the
elements. When in P
ik
one moves from a class C
1
to
a class C
2
by a direct property, we only insert the
descent operator // between the corresponding
elements into P
i
. If one moves from C
1
to C
2
by an
inverse property, then the situation is more
complicated. In most circumstances the query must
be rewritten in depth.
At the end of this stage one can obtain several
rewritings for a query.
7 PROTOTYPE AND
EXPERIMENTS
The prototype which we built implements the
architecture presented in figure 1. We incorporated
the tool SAXON-B (Saxon) to access the OWL
representations. We used the ontology WORDNET
as the domain ontology. Since WORDNET is in fact
a general ontology, we shall use sources for our
experiments which do not contain highly specialized
terms. Access to WORDNET is made through the
JAVA API Java WordNet Library (JWNL). The
body of the matcher is written in JAVA. We have
implemented the two matching functions described
in section 5. However we did not generate the
rewritings that require ascents in the XML files.
Our experiments were conducted on source A
already presented in figure 4 and on source B
presented in figure 7.
We have submitted different queries to the
prototype. We show the results obtained with the
two sources A and B.
Query 1 :
{order[customer/name="Pierre"]/product[price>15]}
Rewritings for source A:
1: {//ORDER[.//CUSTOMER//NAME = "Pierre"]
//PRODUCT[./@price>15]}
Rewritings for source B:
1:
For this query the matcher proposes a correct
rewriting for source A. It does not use any synonyms
or hyponyms. No rewriting is proposed for source B.
Query 2 : {for $a in supplier where
$a/nation="FRANCE" return $a}
Rewritings for source A:
1: {for $a in //SUPPLIER where $a//NATION =
"FRANCE" return $a}
Rewritings for source B:
1: {for $a in //PROVIDER where $a/@Nation =
"FRANCE" return $a}
In source A, NATION is an element and in source B,
it is an attribute. In both cases, the matcher provides
the correct rewriting.
Query 3 : {for $a in supplier, $b in manufacturer
where $a/name=$b/name and $a/nation =
"FRANCE" return $a}
Rewritings for source A:
1: {for $a in //SUPPLIER, $b in
//MANUFACTURER where $a/@name =
$b/@name and $a//NATION = "FRANCE" return
$a}
Rewritings for source B:
1:
For source B, the matcher does not provide any
rewriting. For source A, it proposes a unique
pertinent rewriting.
A rewriting such as:
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
10
{for $a in //SUPPLIER, $b in //MANUFACTURER
where $a//REGION/@name = $b/@name and
$a//NATION = "FRANCE" return $a}
is provided by our matching algorithm. This
rewriting comes from the fact that there exists
another attribute “name” of element REGION which
can be reached from SUPPLIER. This rewriting
contains strictly rewriting 1 and is not pertinent for
the user. It is filtered in an additional step by using
the following rule: “if a rewriting path P1 is a sub-
path of another rewriting path P2 with the same
starting node, delete P2 from the set of solutions”.
Query 4 : {for $a in person, $b in supplier where
$a/name=$b/name return $a}
Rewritings for source A:
1: {for $a in //MANUFACTURER, $b in
//SUPPLIER where $a/@name = $b/@name return
$a}
2: {for $a in //CUSTOMER, $b in //SUPPLIER
where $a//NAME = $b/@name return $a}
3: {for $a in //NAME, $b in //SUPPLIER where $a
= $b/@name return $a}
Rewritings for source B:
1: {for $a in //PERSON, $b in //PROVIDER where
$a/@Name = $b/@Name return $a}
The matcher provides three rewritings for source A
since SUPPLIER, MANUFACTURER, NAME are
hyponyms of PERSON (at level 3). The rewritings 1
and 2 are both pertinent and have immediate
interpretation for a user. Rewriting 3 can surprise a
user. It comes from the ambiguity of using in the
schema of source A an element such NAME which
is a hyponym of PERSON. In fact this rewriting is
redundant with rewriting 2: its path is a sub-path of
rewriting 2 and both terminate at the same element.
So, rewritings 2 and 3 give the same result when
executed on the source. We can use another filtering
rule based on sub-paths. In this case we eliminate
the rewriting 2 and keep only the rewriting 3.
Rewritings such as:
{$a in //MANUFACTURER, $b in //SUPPLIER
where $a/@name = $b//REGION/@name return $a}
are provided by our matching algorithm. Like for
query 3, there are filtered in the additional step.
Our matcher filters also rewritings such as: {for
$b in //SUPPLIER, $a in //SUPPLIER where
$a/@name = $b/@name return $a} which are correct
but which correspond to a truth assertion and do not
give pertinent results.
If we use only the hyponyms of level 1 for this
query, the matcher give no answer for source A.
This example shows clearly the interest of
hyponyms, but also the problems which they can
pose when confronting it to ambiguous schemas.
For source B the matcher provides a unique
rewriting which is pertinent.
8 CONCLUSION AND
PERSPECTIVES
Through the results obtained, it appears that our
mediation system is able to find data from an
intuition of the user, intuition expressed through an
implicit vision of the domain compatible with the
ontology.
The main difficulty results from the fact that the
system generally proposes several rewritings for a
query. Not all these rewritings are relevant. We have
suggested a filtering based on sub-paths to treat this
problem. But this rule cannot solve all the situations.
One can also act on the exploration depth in the
ontology. We have also noticed that some terms
Figure 7: The semi-structured source B.
MEDIATION WITHOUT A GLOBAL SCHEMA - Matching Queries and Local Schemas Through an Ontology
11

(name, number) contribute to increase the number of
irrelevant solutions. It would so be necessary to
minimize their use in the database schemas and to
resort to more precise terms. The quality of the
ontology is also highly important to obtain relevant
rewritings. Ontology WORDNET used for our
experiments is too general and contributes to
sending back too many solutions.
More elaborated solutions exist to deal with this
problem. A solution which we are investigating at
present consists in placing annotations in the OWL
representation at the level of classes or properties.
These annotations will be exploited by the matcher
to take into account semantic features (sense of a
term, meaning of a property). These annotations
could be installed manually by the administrator of
the source or automatically by the system by seeking
the opinion of the users when several rewritings are
possible. To help the matching one can ask the user
to clarify his query if the system detects some
ambiguities.
We think that these improvements could result in
an efficient system.
The system can be extended to deal with other
types of sources (relational, object).
The main advantage of our approach is its
robustness with regard to the evolution of sources.
When a new source is inserted, it is sufficient to
elaborate its OWL representation so that it can be
exploited by the system. When a source evolves, it is
sufficient to reshape its OWL representation.
We are also engaged in another improvement of
our prototype in order to allow the join of results
coming from different sources. In that case a query
is rewritten in several sub-queries, each sub-queries
being relative to a different source. Our matching
algorithm can be easily adapted for this more
general situation. It is necessary to look for sub-
paths in different sources and to impose a join
condition between sub-paths (the terminal node of a
sub-path must be compatible with the start node of
another sub-path).
Such a system can be very useful for different
applications. Incorporated into an intranet system, it
would allow a user to reach the data sources without
knowing their schemas, by being based only on the
domain ontology. In a P2P system, it could be
installed on some peers or on the super-peers to
facilitate access to data by their semantics. The only
obligation for a peer would be to publish its data by
using the OWL representation.
REFERENCES
Bernstein P. A., Melnik, S., Petropoulos M., and Quix C.,
2004. Industrial-strength schema matching. SIGMOD
Record, 33, 4. pp 38-43.
Cui Z., Jones D., O’Brien P., 2001. Issues in Ontology-
based Information Integration. IJCAI, Seattle, August
5 2001.
Garcia-Molina H., Papakonstantinou Y., Quass D.,
Rajaraman A., Sagiv Y., Ullman J., Vassalos V. and
Widom J.,1997). The Tsimmis approach to mediation:
Data models and languages. Journal of Intelligent
Information Systems , Vol. 8, No. 2. pp. 117-132.
Hai Do H., Melnik S., Rahm E., 2002. Comparison of
Schema Matching Evaluations. Web, Web-Services,
and Database Systems. pp 221-237.
Hull R., 1997. Managing semantic heterogeneity in
databases: A theoretical perspective. Proc. of the
Symposium on Principles of Database Systems
(PODS), Tucson, Arizona . pp. 51-61.
JWNL. Java WordNet Library.
http ://sourceforge.net/projects/jwordnet.
Kedad Z., Métais E., 1999. Dealing with Semantic
Heterogeneity During Data Integration. Proc of the
International Entity Relationship Conference. pp. 325-
339.
Mohsenzadeh M., Shams F., Teshnehlab M., 2005.
Comparison of Schema Matching Systems. WEC (2).
pp 141-147.
Lenzerini M., 2005. Logical Foundations for Data
Integration. SOFSEM 2005. pp 38-40.
Missikoff M., Taglino F., 2004. An Ontology-based
Platform for Semantic Interoperability. Handbook on
Ontologies. pp 617-634.
Rahm E ., Bernstein P.A., 2001. A survey of approaches to
automatic schema matching. VLDB Journal 10(4). pp
334-350.
Saxon. SAXON: The XSLT and XQuery Processor.
http://saxon.sourceforge.net/.
Wache H., Vogele T., Visser U., Stuckenschmidt H.,
Schuster G., Neumann H. and Hubner S., 2001.
Ontology-based integration of information - a survey
of existing approaches. In Stuckenschmidt, H., ed.,
IJCAI-01 Workshop: Ontologies and Information
Sharing. pp 108-117.
Wiederhold G., 1992; Mediators in the architecture of
future information systems. IEEE Computer, Vol. 25,
No.3. pp.38-49.
WEBIST 2006 - INTERNET TECHNOLOGY
12
